To launch Ansys Workbench on Windows, click the Start menu, then select All Programs > Ansys 2024 R2 > Workbench 2024 R2.
Note: For CFX, TurboGrid and CFD-Post applications, the graphics viewer, which is based on OpenGL 4.5, will work with
Microsoft Windows Remote Desktop Connection only if you are using Nvidia Quadro graphics cards with appropriate drivers for Windows 10.
If you see an empty (black) viewer, try setting the environment variable CFX_QT_OPENGL=desktop on the remote machine,
in the local environment of the intended application (for example, in a shell or script that launches the application),
before starting the application. Consider adding this environment variable to the cfx5rc.txt user’s configuration file.
To work around this issue you may launch the CFX application prior to making the remote connection,
or use one of the other Ansys-supported remote display methods.
To launch Ansys Workbench on Linux, open a command line interface, type the path to "runwb2" (for example, "~/ansys_inc/v242/Framework/bin/Linux64/runwb2"), then press Enter.
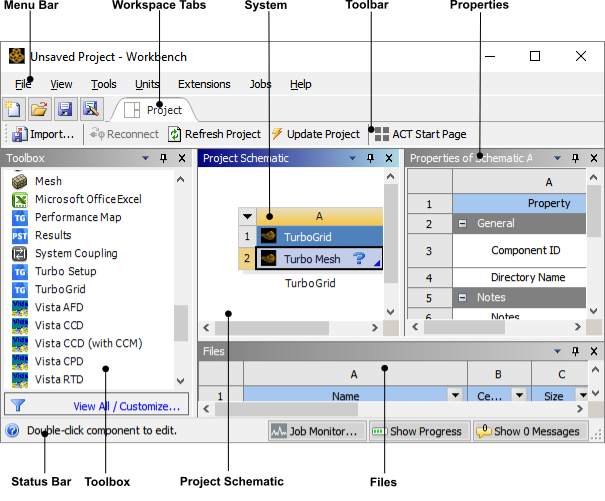
The Ansys Workbench interface is organized to make it easy to choose the tool set that will enable you to solve particular types of problems. Once you have chosen a system from the Toolbox and moved it into the Project Schematic, supporting features such as Properties and Messages provide orienting information. These features and the status indicators in the system cells guide you through the completion of the System steps.
The figure that follows shows Ansys Workbench with a TurboGrid component system open and the properties of cell A2 (Turbo Mesh) displayed:
The following sections describe the main Ansys Workbench features.


