VM-LSDYNA-SOLVE-008
VM-LSDYNA-SOLVE-008
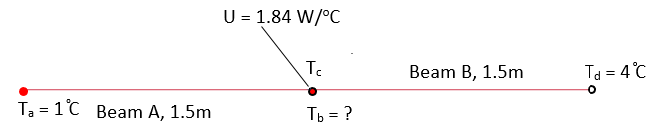
Steady State Thermal Analysis of a Beam
Overview
| Reference: | Kreith, F. (1959). Principles of Heat Transfer (2nd ed.). International Textbook Co. |
| Analysis Type(s): | Steady State Thermal |
| Element Type(s): | Beam |
| Input Files: | Link to Input Files Download Page |
Test Case
Isotropic steel beams A and B are separated by an area with thermal conductance U = 1.84 W/°C. Beams A and B are of equal length L = 1.5 m, thermal conductivity k = 46 W/(m°C), and cross-sectional area A = 0.04 m2. The far end of beam A has a temperature of 1°C. The opposite end of beam B has a temperature of 4°C. Find the steady state temperature Tb on beam A.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading |
|---|---|---|
| k = 46 W/(m°C) | Lab = 1.5 m | Ta = 1°C |
| U = 1.84 W/°C | Lcd = 1.5 m | Td = 4°C |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
LS-DYNA Thermal Solver 3 is used. The steel beams are modeled using ELFORM 1. Conduction between beams is constrained using a zero-length discrete beam with ELFORM 6. Temperature boundary conditions are applied using keyword *BOUNDARY_TEMPERATURE.
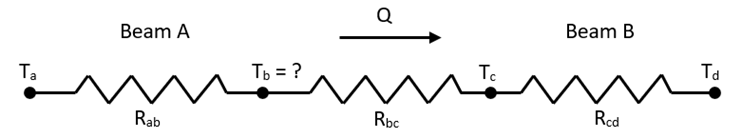
At steady state, the rate of heat dissipation Q
And the thermal resistances Rab, Rcd, and Rbc can be expressed as:
From the above equations, the analytical solution of Tb is obtained as 2.125°C.