VM-LSDYNA-BENCHMARK-004
VM-LSDYNA-BENCHMARK-004
Combined Stress in Lever
Overview
| Reference: | Beer, F. & Johnston, E. (1992). Mechanics of materials (2nd ed., p.348). McGraw-Hill, Inc. |
| Analysis Type(s): | Explicit Dynamics with Workbench LS-DYNA |
| Element Type(s): | Solid |
| Input Files | Link to Input Files Download Page |
Test Case
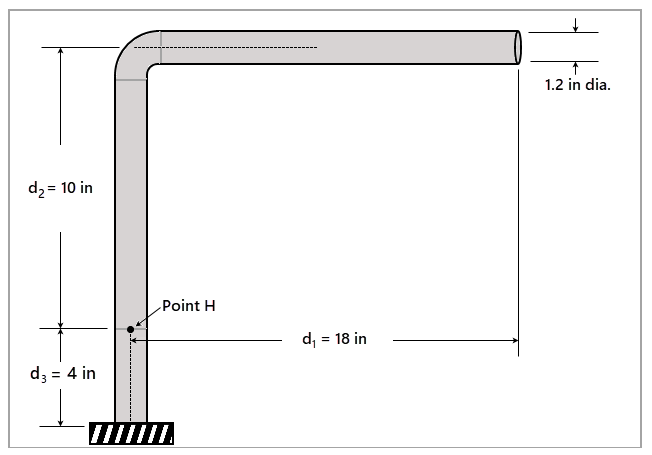
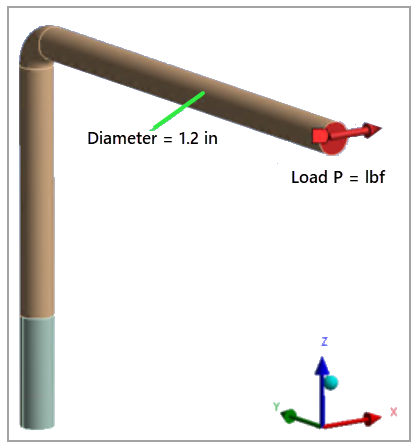
An L-shaped lever in the yz plane with a constant, circular cross-section is fixed at one end. A load is applied to the free end in the x direction. A linearly elastic, isotropic material model is used for the beam, with a Young's modulus (E) of 2.90x107 psi and Poisson's ratio of 0.3.
Determine normal stress in z-direction, shear stress in xy-direction, maximum principal stress and minimum principal stress on a point located 4 inches from the fixed end.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading |
|---|---|---|
|
E = 2.9x107 psi ν = 0.3 |
L = 50 in B = 2 in H = 2 in |
P = 150 lbf |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The closed form solution equations for the normal stress in y-direction (σy), shear stress in xy-direction (τxy), maximum principal stress (σmax) and minimum principal stress (σmin) at Point H are as follows:
Substituting for the given values above, σz = 8.842 ksi, τxy = 7.958 ksi, σmax = 13.52 ksi and, σmin = –4.682 ksi.
The LS-DYNA Explicit settings were selected to minimize solution running time but ensure that the output deflection reached a steady state free from vibrations.
The load application was defined over 0.1 seconds (the force was ramped from 0 to 150 lbf over 0.05 seconds then constant for 0.05 seconds).
The Global Damping was defined as 100.
The element used was LS-DYNA Explicit Hex 1 with an element size of 0.1 inch.
Results Comparison values are reported for the Windows 11 platform.