An EnSight context consists of a set of files: the context file itself as well as associated palette, view, and keyframe animation files. The names of the associated files will be that of the context file with a standard extension.
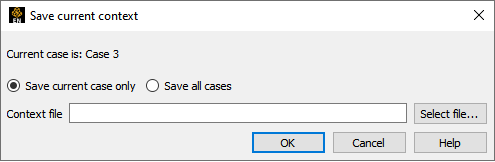
Select → → to open the Save Current Context dialog.
Toggle Save Current Case Only or Save All Cases.
Enter a name for the Context File.
You can set the directory for the Context File by clicking the button to open a standard File Selection dialog.
Click .
Three options:
Start EnSight and restore a context as described below. This will recreate the parts of the original dataset and restore them to their saved condition.
Start EnSight, read a new dataset, cancel the part loader without creating parts, and restore a context as described below. This will create the parts of the new dataset (mapping as directed) and restore the context of the original dataset.
Start EnSight, read a new dataset, create the desired parts, and restore a context as described below. This will do the mapping (as directed) of parts and restore the context of the original dataset.
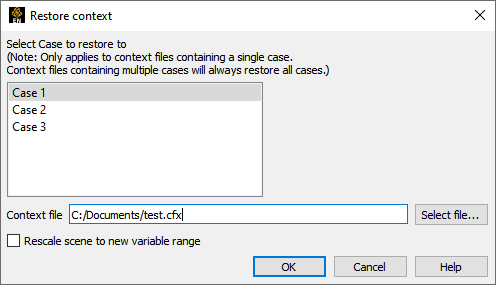
Select > >
Select the case to restore the context to.
Note: If the context file contains information for multiple cases, ignores the selection.
Enter or select the desired context file.
Click .
The same part names (and variable names) do not have to exist in the new case. If this situation arises, a message dialog will appear where you will be asked to match the part names (or variable names) from the context file with the parts (or variables) from the new case. This dialog is not available in batch mode. Therefore, you can't use a context file that needs matching in batch mode. If the number of parts between the two datasets match, then no mapping of parts occurs and the parts will end up renamed to match the original case.
When restoring context files with multiple cases, the needed cases will be started, if needed, according to the connection scheme of the current run of EnSight.
Flipbook animations are not restored using the context file because it is unknown at the time the context file is created what state existed when the flipbook was saved.
If data is not read before restoring the context file, the data that was used when the context file was saved will be loaded.
Context files use EnSight's command language and other state files (such as palette, view, and keyframe animation) to recreate the parts, variables, and view state.


