Writing a Script
Intellisense
Intellisense, or intelligent code completion, is included in the editor to assist with entering commands. It is a context-aware code completion feature that improves the process of coding applications by reducing typos and other common mistakes. The code completion and related tools serve as documentation and disambiguation for variable names, functions, and methods using reflection.
When you type in the Script Editor, you will see suggestions for commands, helper functions, and variables (created or with Smart Variable Selection).
Auto complete features add parentheses when writing functions in the Script Editor. For-loops can be created automatically.
The example shows the import of the CustomProperty API. Start by typing in the Script Editor and click the All tab to see all suggestions.
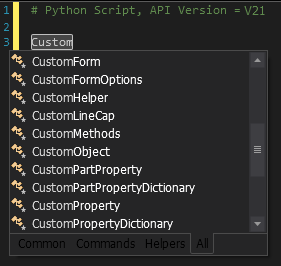
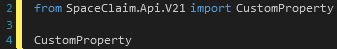
Select CustomProperty from the list. The API is then imported into the script as shown.
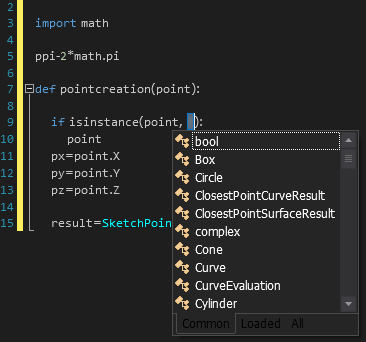
Use Cast and CastCheck with expressions or variables.
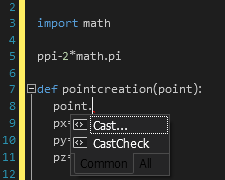
Cast enables you add a type to an expression. For example, you can declare a variable and set its type in the Scripting Tool.
Note that when you cast a variable inside of a method, it is only cast to that type inside the method.
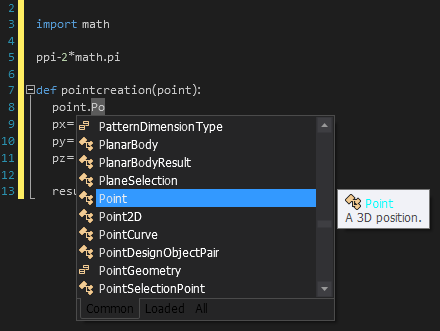
CastCheck enables you to check the type of expression by surrounding it with an if-statement. Once a variable is cast, you can choose to add a CastCheck, which adds an if-statement to the code. This if-statement allows you to confirm the variable's type before performing additional calculations or modifications.
Selection Converting and Filtering
To improve selection in scripting, created selections can be converted or filtered based on size, geometry, or other requirements.
For each of the selections, you can choose from the Filter and Convert methods available. For example, you can choose to filter faces, edges, parts, bodies, or components. You can convert selections to types (such as faces or edges), or convert by shape, size, etc.
For example, you can get the root part of the assembly, convert that selection to edges, and then filter by size:
Power Selection and Smart Variables
Power Selection is recorded and, when using Smart Variables, can be used to perform similar operations on multiple bodies.
For example, you can record the power-selection of holes with a certain diameter, and then the filling of those holes with the Fill tool. That script can then be used to fill holes of the same size in other models, even if the number of holes is different.