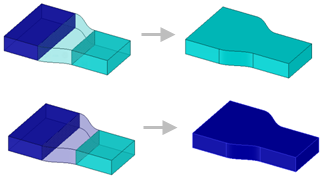
Blend Tool Options
The following options are available in the Blend tool Options panel when you select the appropriate geometry for a blend.
| Rotational blend | Create cylinders and cones whenever possible during the creation of a blend. You must have selected faces, points, or edges that can be rotated around a common axis. | |
| Periodic blend | Go all the way around when blending. The blend will begin and end at the first selected object. You must have selected three or more faces, points, or edges that can be rotated around a common axis, and that also span an arc greater than 180 degrees. (Blending between 3 equal-radius circle faces creates a torus.) | |
| Ruled sections | Create straight edges when you blend. When you blend between faces, this option has the same affect as selecting the face and its edges. | |
| Local guides | Selected guide curves only influence areas near to them. | |
| Minimal topology | Create a smooth face blend without unnecessary faces or edges for closed profiles with smooth vertices. | |
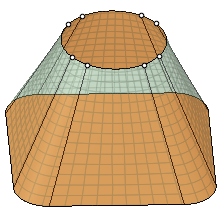
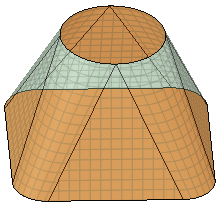
| Sheet metal blend |
Forces the tool to create developable surfaces. A developable surface is defined in mathematics as a surface with zero Gaussian Curvature (that is, a surface that can be flattened into a plane). The tool attempts to create planes, cylinders, and cones, in that order to maximize the planar areas. It is restricted to blending between two parallel planes. |
|
|
Sheet metal blend unchecked.
|
Sheet metal blend checked.
|
|
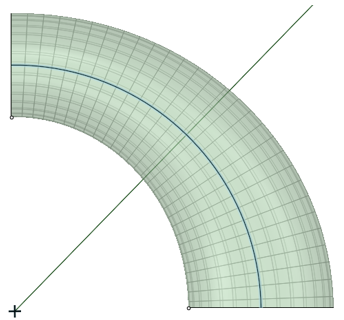
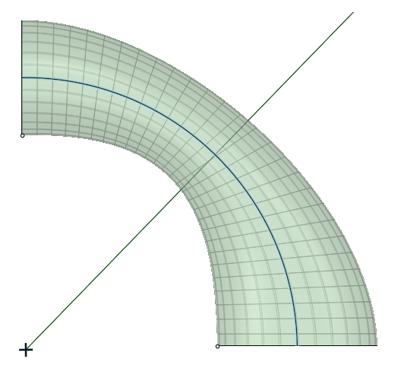
| Normal to Centerline |
When on by default, Normal to Centerline forces the Blend algorithm to keep sections normal to the centerline. When off, the algorithm has more freedom to adjust sections so that a surface can be created. |
|
|
Normal to centerline On.
|
Normal to centerline Off
|
|
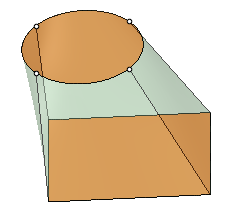
| Show UV grid |
This option is ON by default to help visualize contours by
displaying a grid on the preview. Use the dropdown slider to
increase or decrease the density of the grid.
|
|
Example