VM142
VM142
Stress Concentration At a Hole in a Plate
Overview
Test Case
Determine the maximum stress at a circular hole cut into a square plate loaded with uniform tension P.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
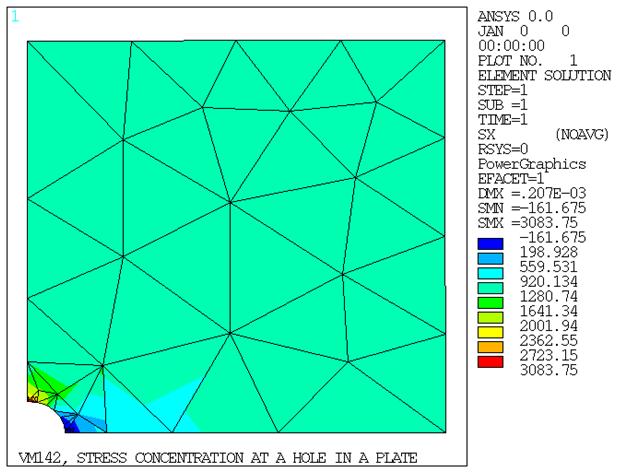
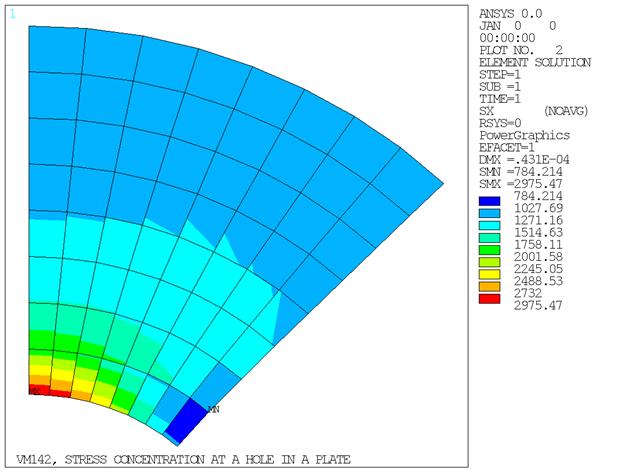
Due to symmetry, only a quarter sector of the plate is modeled. Mesh generation is used for node and element creation. The area around the hole is remodeled with a fine mesh and boundary conditions are interpolated from the first model by use of the cut-boundary interpolation capability (CBDOF) in POST1.
Results Comparison
| Target | Mechanical APDL | Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse Model | stressx max PLANE183 | 3018 | 2721 | 0.902 |
| Submodel | stressx max PLANE182 | 3018 | 2975 | 0.986 |
Max σx based on estimated bounds due to discretization error for the coarse model and submodel are 2855. and 3076. respectively.
The coarse PLANE183 model is offered for comparison with the submodel. Coarse PLANE183 results may vary across platforms.