YNI Contributions
This feature lists for each surface the paraxial YNI value, which is proportional to the Narcissus contribution of that surface.
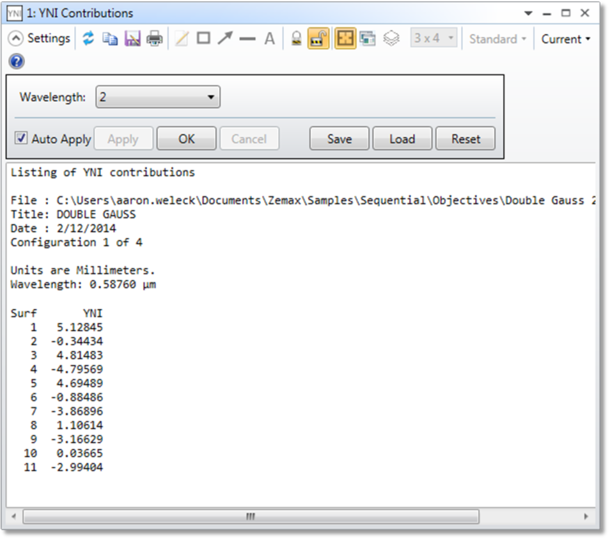
Wavelength The wavelength number to use for the calculation.
Discussion In sequential mode, the YNI Contributions analysis and YNIP operand give first-order approximations to the Narcissus contribution of the surface.
The YNI contribution of each surface is the product of the paraxial marginal ray height times the index times the angle of incidence at the surface defined by Surf at the wavelength defined by Wave. This quantity is related to the Narcissus contribution of the specified surface.
The following equation shows the cold return for on-axis image for a single surface in the system. The Narcissus intensity is proportional to the summation of cold return of all refractive surfaces. Therefore, to reduce the Narcissus intensity, the YNI needs to be as large as possible.
For a more detailed discussion, see "Narcissus: reflections on retroreflections in thermal imaging systems," Applied Optics, Vol. 21, No. 18, p3393 (1982).
Next:


