Longitudinal Aberration

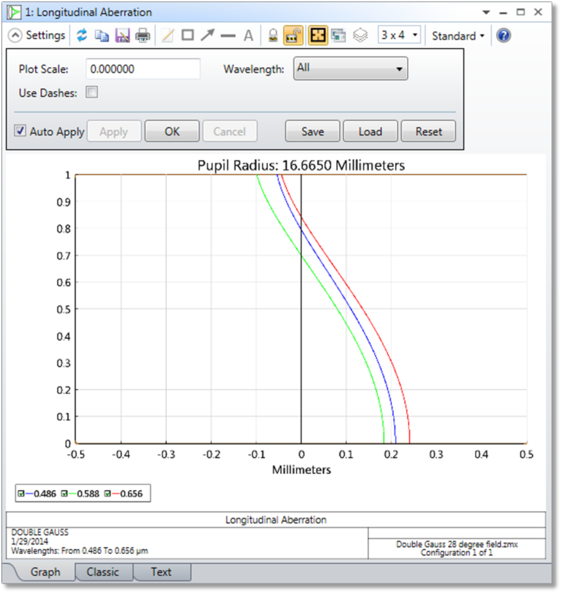
Displays the Longitudinal Aberration as a function of pupil height at each wavelength.
Plot Scale Defines the maximum scale for the plot in lens units. Enter zero for automatic.
Wavelength The wavelength number to be used in the calculation.
Use Dashes Selects either solid lines or dashed lines to differentiate the various curves.
Discussion This feature computes the distance from the image surface to where a zonal marginal ray "focuses", or crosses the optical axis. The computation is performed only for the on axis field point, and only for zonal marginal tangential rays as a function of pupil zone. The base of the plot is on axis, and the top of the plot represents the maximum entrance pupil radius. There are no units on the vertical scale because the plot is always normalized to the maximum entrance pupil radius. The horizontal scale is in lens units, and represents the distance from the image surface to the point where the ray crosses the optical axis. For afocal systems, the horizontal axis is diopters of power required to bring the rays to collimation.
Because longitudinal aberration is defined in terms of the distance to the ray-axis crossing point, this feature may produce meaningless data for non-rotationally symmetric systems. Great care should be exercised in interpreting this plot for non-rotationally symmetric systems.
Next:


