Geometric MTF

Computes the geometric MTF, which is an approximation to the diffraction MTF based upon ray aberration data.
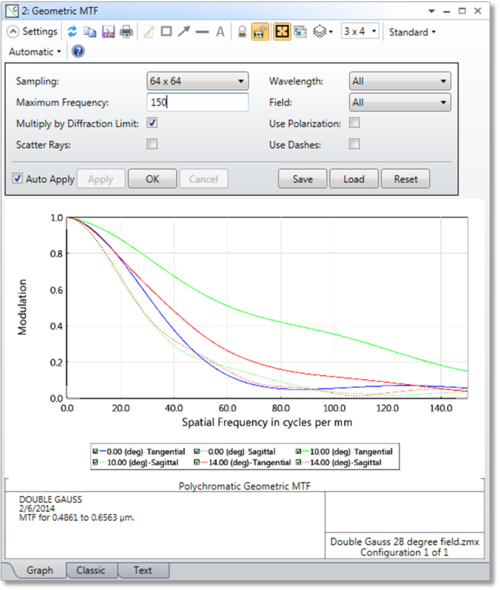
Sampling The size of the ray grid used to sample the pupil. The sampling may be 32x32, 64x64, etc. Although higher sampling yields more accurate data, calculation times increase.
Max Frequency The maximum spatial frequency (see "MTF Units") for which data is plotted.
Wavelength The wavelength number to be used in the calculation.
Field The field number for which the calculation should be performed.
Multiply by Diffraction Limit When checked, will scale the geometric MTF by the diffraction limited MTF to yield a more realistic result for systems with small aberrations. Should always be used.
Use Polarization If checked, polarization is considered.
See " Polarization (system explorer)" for information on defining the polarization state and how polarization is used by analysis features.
Scatter Rays If checked, rays will be statistically scattered at ray-surface intercepts that have defined scattering properties. See "Scattering (surface properties)"
Use Dashes Selects either solid lines or dashed lines to differentiate the various curves. This setting only applies to the Classic view, which is an option if "Enable Classic View" is selected in the Graphics tab of the OpticStudio Preferences.
Discussion
The geometric MTF is a useful approximation to the diffraction MTF if the system is not close to the diffraction limit. The primary advantage to using the geometric MTF is for systems which have too many waves of aberration to permit accurate calculation of the diffraction MTF. The geometric MTF is also very accurate at low spatial frequencies for systems with large aberrations.
The nature of the geometric algorithm is that the computation is done in image space coordinates. For this reason, rotating the image surface will affect the orientation of the computed MTF. The tangential response corresponds to the image of a periodic target oriented with lines along the image space X axis, and the sagittal response corresponds to the image of a periodic target oriented with lines along the image space Y axis. This is different from the conventions of the "FFT MTF"
Next:


