Create and Use Parametric Array in SBR+ Simulation
This chapter provides a summary and a detailed workflow for using Parametric Antenna Arrays for SBR+ simulation.
Summary Workflow for Parametric Antenna Arrays
- Create an HFSS design and select the SBR+ Solution Type.
- Add model objects, components.
- Add an antenna local coordinate system .
- Add the parametric antenna array by right-click on 3D Components in the Project tree and select Create Antenna>Parametric Array… or right click on Excitations in the Project tree and select Create Antenna Component>Parametric Array....
- In the Create Parametric Array dialog
- Select the array element type
- Configure geometry conformance for the array.
- Configure the array element
- Configure the array layout geometry
- Configure the array weighting
- Configure any component instance parameters for the array component
- Visualize a preview of the array layout geometry and array pattern
- Close the dialog with OK to save and create the parametric array 3D component
- Place and orient (Translate, Rotate) the 3D component at the desired geometry location
- Optionally modify the 3D component definition in the model tree
- Optionally modify the 3D component instance in the project tree
- Add an Analysis Setup
- Run simulation
- Generate far field radiation pattern
Detailed Workflow for using Parametric Antenna Arrays in SBR+ Simulation
- Create an HFSS design and select the SBR+ Solution Type.
- Add model objects, components.
-
Add an antenna local coordinate system. Creation of an antenna local coordinate system (CS) can be very useful in placing and orienting parametric antennas and arrays via 3D components. The CS can be created as a simple relative CS, or as something more advanced and suitable for array placement on a surface, like a face CS . After creating the new CS, make sure it is selected/active when creating the parametric array.
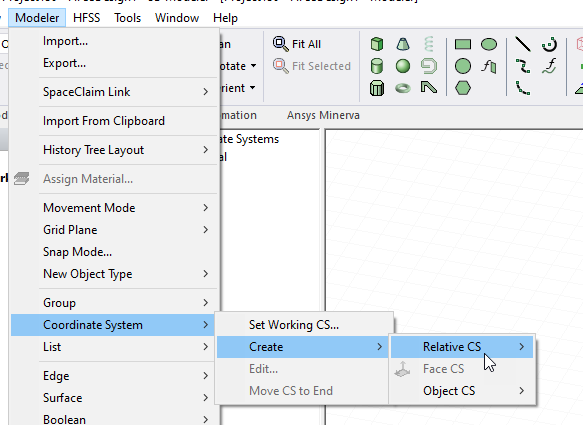
- Add the parametric antenna array by right-click on 3D Components in the Project tree and select Create Antenna>Parametric Array… or right click on Excitations in the Project tree and select Create Antenna Component>Parametric Array....
This opens the Create Parametric Array dialog box. This figure shows the appearance with Options>HFSS>Boundary Assignment Use wizards for data input when creating new boundaries checked. You can choose to view this information as either a wizard or as a multitab dialog.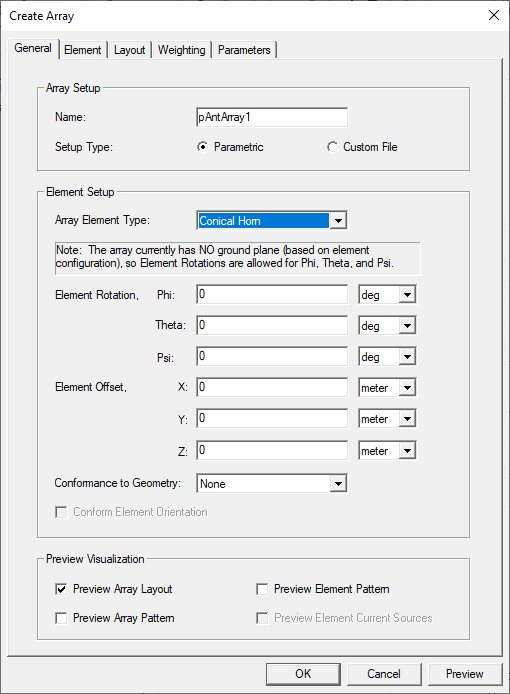
- In the Create Parametric Array dialog
- Select the Array Element Type of antenna from the drop-down menu. You can select any of the fourteen parametric antenna types as the Array Element.
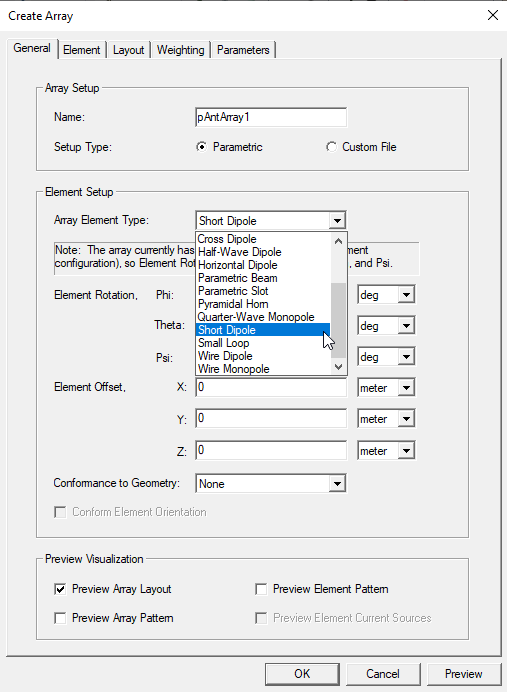
Specify the Element Rotation for Theta and Phi and select the units from the menus. Click Preview for a display in the Model window.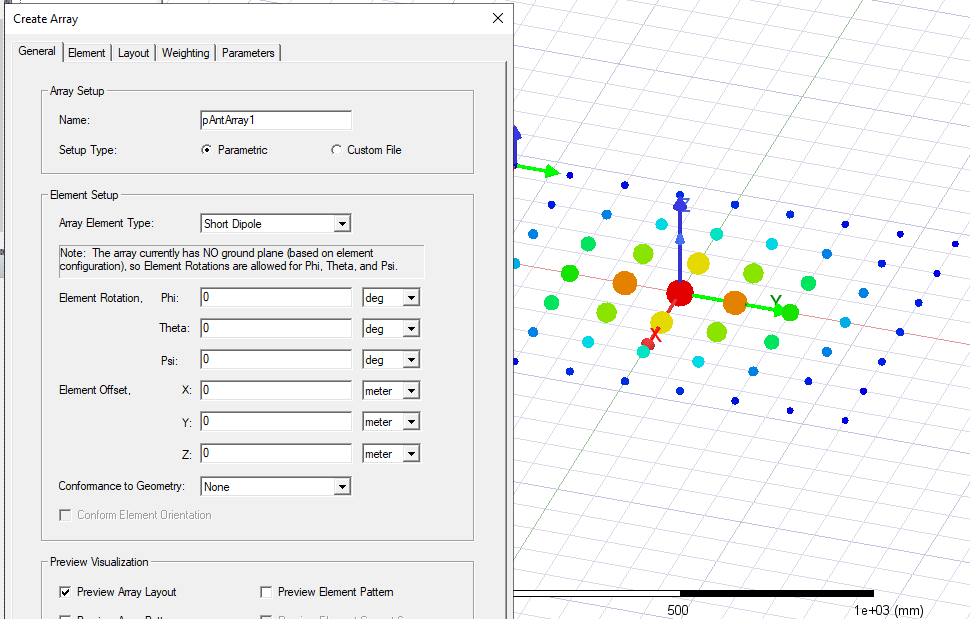
- You can also specify an Element Offset for X, Y, and Z, and specify Units. After you have specified a value, and the cursor to another text box, the Preview button is enabled, allowing you to view the visualization for the values you have specified.
- Use the checkboxes to Preview Array Layout, Array Pattern, Element Pattern, and Current Sources (when an element type with current sources is selected). The next figure shows both Array Layout and Array Pattern after clicking Preview.
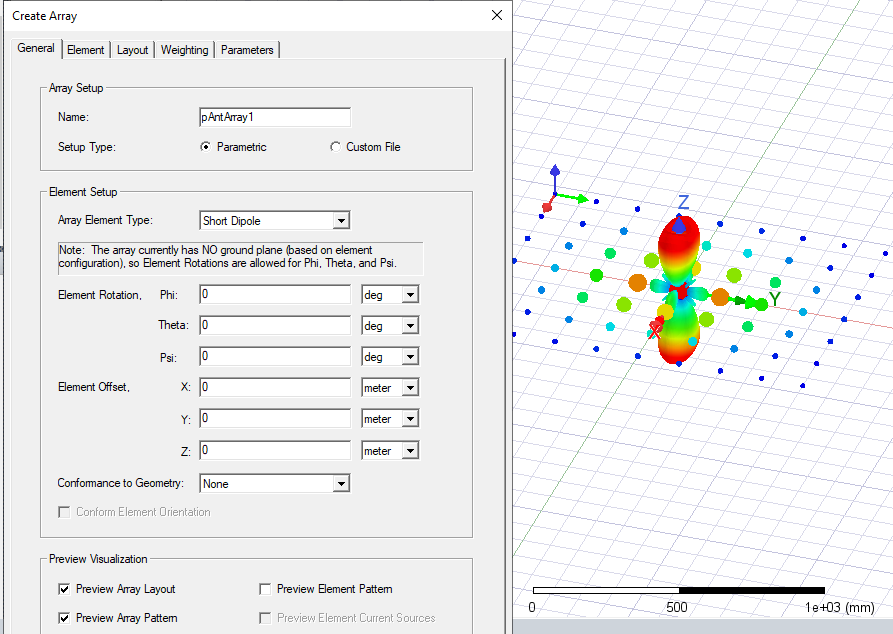
The next figure shows the scaled far field pattern of the antenna array, and then clicking Preview.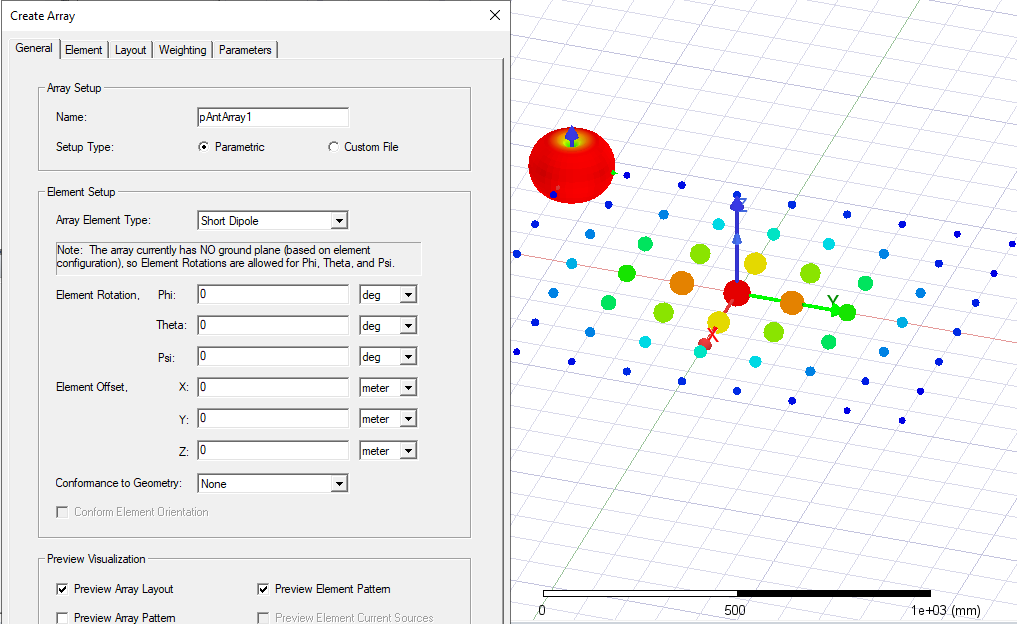
- You can use the Conformance to Geometry dropdown to select None, Along Normal, or Perpendicular to Plane. Making the selection Along Normal enables the Conform Element Orientation checkbox.
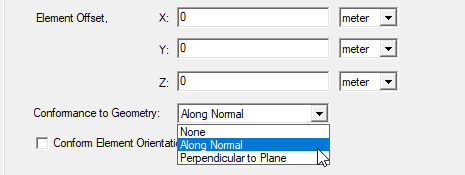
The following figure shows Conformance Along Normal relative to a sphere.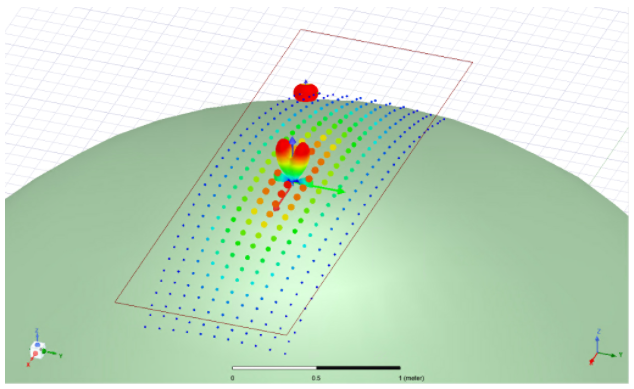
For a technical discussion, see Technical Notes: Current Conformance in SBR+. - Configure the array element. The parameters available on the Element tab (or the Element wizard page) will vary depending on the Antenna Element Type chosen. For example, the Short Dipole antenna only shows the Array Element Type as Short Dipole with no additional parameters, since this simple antenna element type has no parameters to configure. Most of the antenna element types will have some additional parameters to configure on this tab/page.
The Cross Dipole Element tab shows the same parameters as the Cross Dipole Parametric antenna. Component variables may be defined for many of the antenna array properties. If you specify variables for any of the parameters, these will be displayed in the Parameters tab.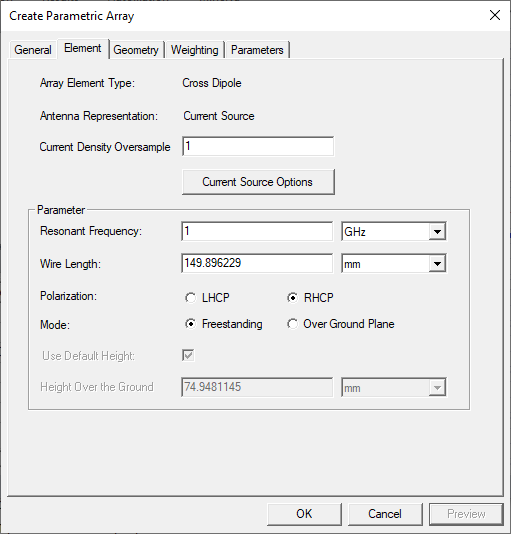
- Configure the array layout geometry. The array layout geometry is defined in the XY plane of the placement coordinate system as Rectangular, Elliptical, or Linear, and is parametrically defined by array Length, Width, Length/Width Element Spacing, and various other adjustments for the element placement geometry. The geometry layout parameters may be specified in user-selectable units or in units of wavelength, as determined by the Design Frequency. Selecting Enforce Symmetry along either/both axes ensures that no elements are placed directly on the axis of symmetry, essentially constraining the number of element rows or columns to be "even".
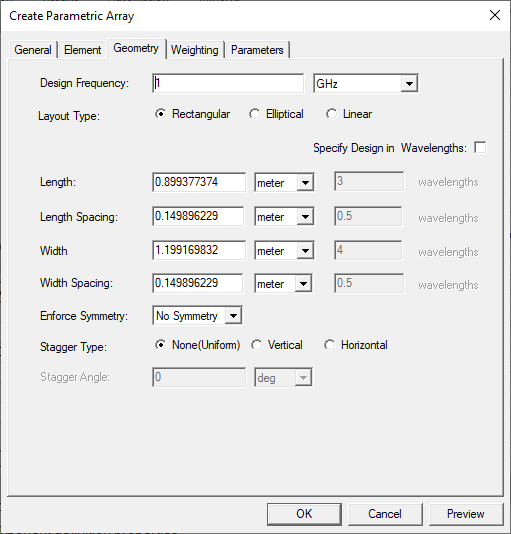
Click the Preview button to view the effects of your selections. The following example shows a Preview for selecting the Layout Type as Elliptical.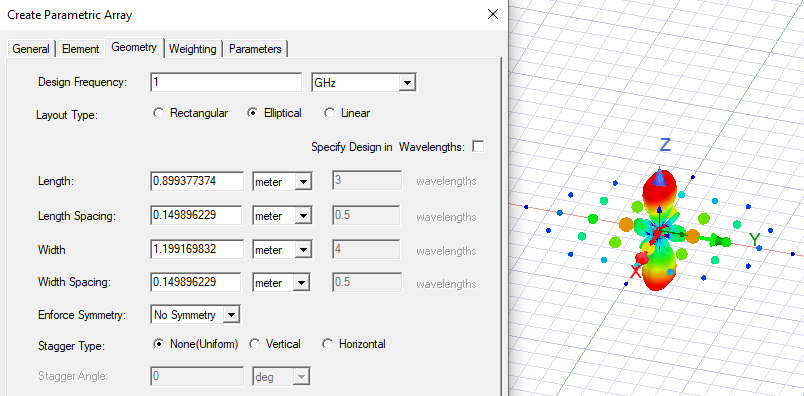
- Configure the array weighting. You can specify Beam Steer, Aperture Taper and Sum/Difference Pattern.
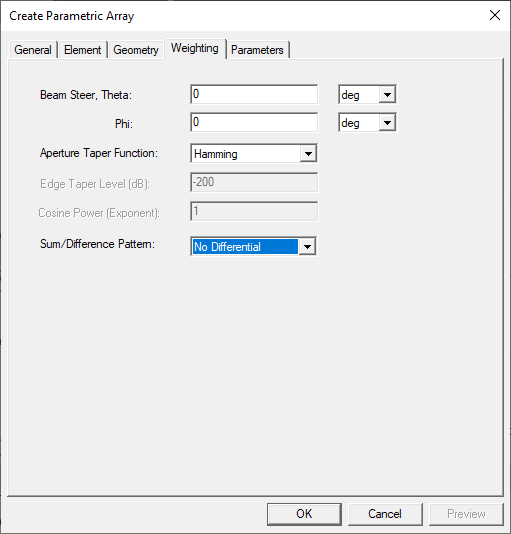
You can specify values as variables. For example.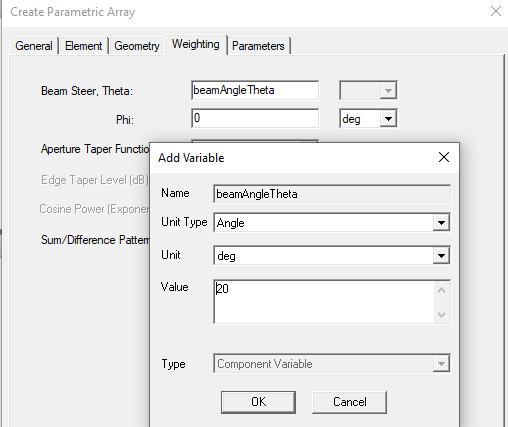
- If you have specified any values for the Parametric Antenna as variables, these appear on the Parameters tab. For example, if on the Weighting tab you specified beam steer for Theta and Phi as variables, they would appear as shown.
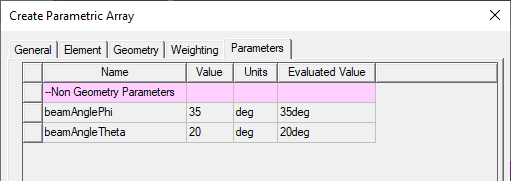
You can configure any component instance parameters for the array component. These can be mapped to design/project variables. - As previously referenced, the Preview button can be used to visualize the array layout, element pattern, and resulting array antenna pattern, including any ground plane requirement for the selected Array Element Type. Any changes made to the array property tabs/pages will enable the Preview button. Clicking Preview applies the changes in the modeler window and disables the Preview button.
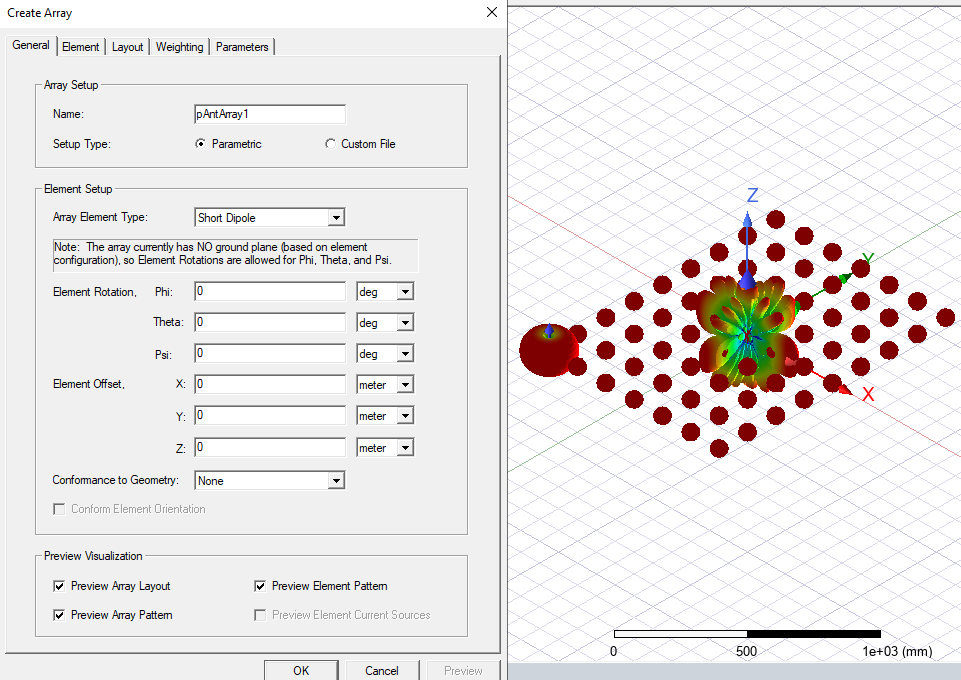
Close the dialog with OK to save this component definition and create the parametric array 3D component instance.
- Select the Array Element Type of antenna from the drop-down menu. You can select any of the fourteen parametric antenna types as the Array Element.
- If you want to edit the antenna placement, or orientation, select the model in the History tree, and right-click and select Edit>Arrange, and select from Move, Rotate, or Mirror. When you select the Parametric Array, the icons in the ribbon are also enabled.
If needed, place and orient (Move, Rotate, Mirror) the 3D component at the desired geometry location.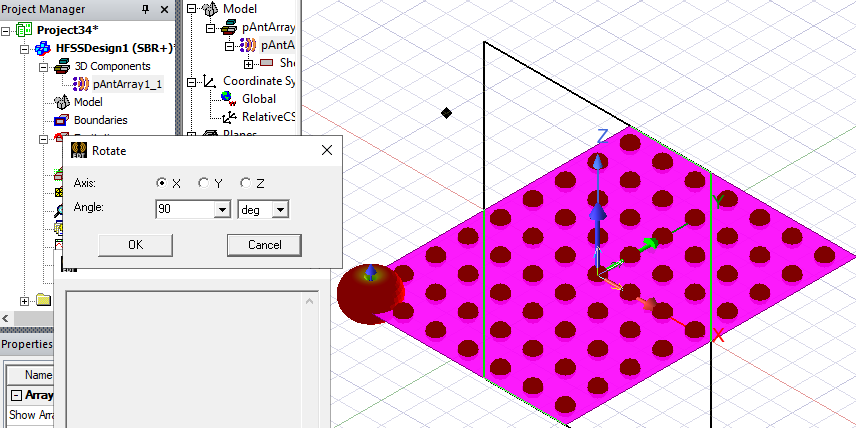
Notice that other edit commands for Copy, Paste, and Duplicate are also available. You can also change or edit the target coordinate system in the instance Property window.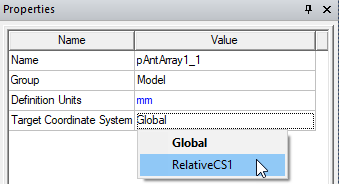
- You can view and edit the 3D component definition in the History tree. Selecting the 3D Component and Edit Properties opens the Create Parametric Array dialog and lets you edit the Properties as you did in creating the Parametric array.
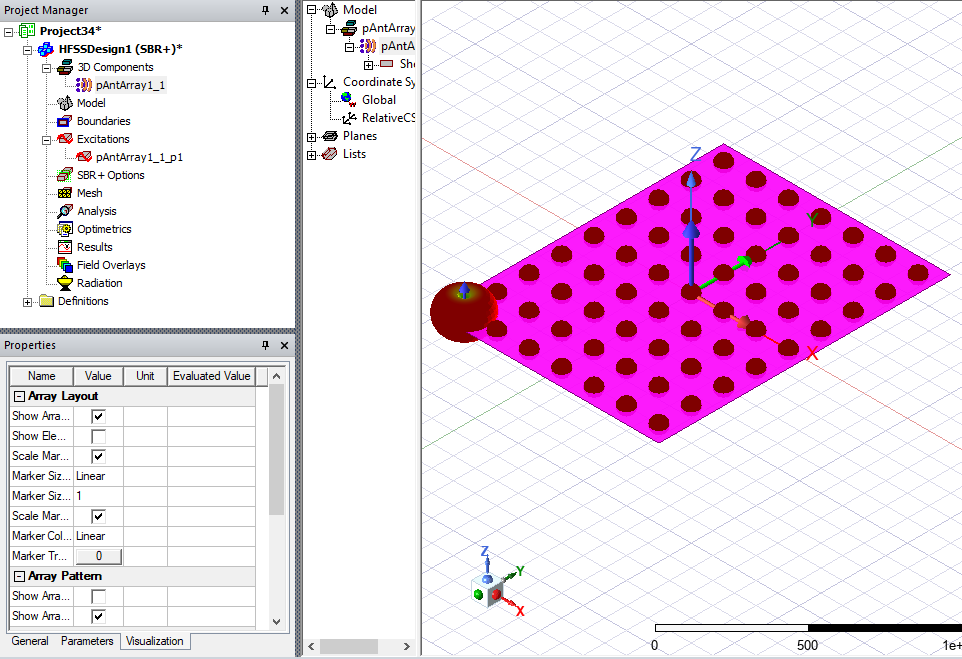
- You can view and edit the properties of the 3D Component instance listed in the Project tree. Select an array antenna instance listed under 3D Components, or in the Model tree listed under one of the created Model component definitions. For each component instance that is created, there are unique instance-level properties separate from the array geometry/weighting definition that can be configured for visualization, etc. They are grouped into 3 separate tabs for General, Parameters, and Visualization.
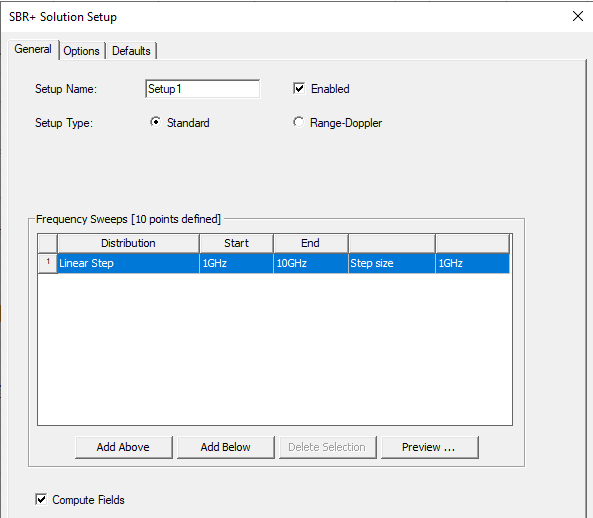
- Add an SBR+ Solution Setup. To generate a far field radiation pattern for this parametric array, be sure Compute Fields is checked on the General tab.
Also ensure that a far field Observation Domain has been correctly configured.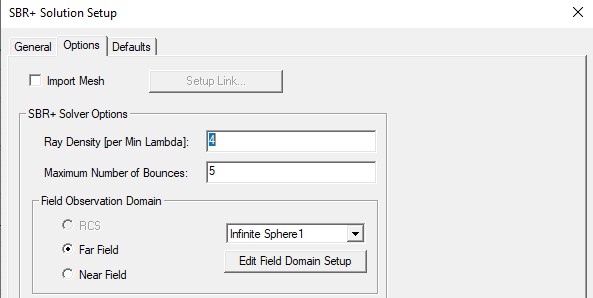
You must create a Far Field Setup to access the Far Fields and Antenna Parameters reports.
-
You may select Use Per-Element Power Specification for a Parametric Array in the Edit Sources dialog when only a Parametric Array exists in the scene. When you select that option, Edit Sources defines the input power of an element before applying the Aperture Taper configured in Array Weightings. The Parametric Array with this option gives results similar to HFSS post-processing feature of Antenna Array. Coupling analysis and Enhanced Radiated Power Accuracy are not supported.

- Run simulation.
- Generate far field radiation pattern. Right-click on the Result node in the Project Manager and select Create Far Fields Report > Radiation Pattern to create a radiation pattern plot for the desired range of theta/phi angles
After you run an SBR+ simulation with parametric antennas, the results available are just like for a single-port parametric antenna. You can create a variety of reports, including S Parameters, Far Fields, and Antenna Parameters.