MATLAB optimizer
The MATLAB optimizer option lets you pass a script to MATLAB to perform the optimization. When optimization starts, MATLAB launches and a script passes in to MATLAB to perform the optimization. During optimization, MATLAB calls back into Twin Builder to perform the solve and compute the cost. The cost is reported back to MATLAB, and MATLAB's optimization then determines the next step in the optimization.
The optimization script is specified as part of the optimization setup. By modifying the optimization script, you can change optimization parameters and optimization method as well as use the full power of MATLAB.
Running the Optimization
A MATLAB optimization launches like any other optimization. The Message Manager pane displays status messages when MATLAB launches, and status messages generate for each solve being performed.
In most cases, MATLAB terminates when the optimization completes. Some reasons why MATLAB may fail to terminate include:
- You have modified the MATLAB script to not terminate MATLAB after the optimization.
- A syntax error or some other error has occurred.
- You have added some other code, which runs after the optimization completes.
System Requirements
In order to use MATLAB to perform optimizations from your application:
- A version of MATLAB must be installed on your system.
- The computing platform (that is, 64-bit) of MATLAB must match the platform of the Ansys application you are using it with.
- You must have the MATLAB Optimization Toolkit installed.
Specifying the MATLAB Location
The Miscellaneous tab at Tools > Options > General Options contains a setting for the MATLAB application location. This setting must point to the version of MATLAB that will perform the optimization. The platform (64-bit) of the specified version of MATLAB must match the platform of this application.
MATLAB Optimization Setup
MATLAB optimization starts by creating an optimization and selecting MATLAB from the optimizer drop-down list. If you select MATLAB as the optimizer, the Setup Optimization dialog box displays a Setup button.
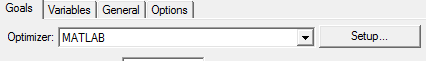
Click Setup to open the MATLAB Options dialog box.
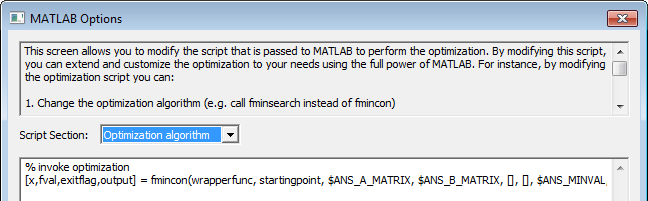
The upper text panel is informative. The Script Section drop-down list lets you select a lower panel display for Optimization algorithm, Options, or the Full script template.
This panel lets you modify the script passed to MATLAB to perform the optimization. The complete script contains all the instructions necessary for MATLAB to connect to Twin Builder and perform the optimization. The drop-down selection lets you view only the portion of code of interest without having to view the full script. The choices are:
- Optimization algorithm – Displays only the line of code invoking the actual optimization function. By changing this line, you can use a different MATLAB function for optimization. By default fmincon() is used, which is a derivative-based constrained optimization. By modifying this line, you could replace the fmincon() call with fminsearch() to use an unconstrained pattern searching optimizer or another optimization function. See the MATLAB documentation for details about available optimization functions.
- Options – Each optimization function contains many options and parameters, which are set in the MATLAB script prior to calling the optimization function. By modifying these options, the optimization can be customized as desired. For instance, options can be set for fmincon() to specify the algorithm that it uses internally. See the MATLAB documentation for details about options available for each optimization function.
- Full script template – This choice displays the full optimization script passed to MATLAB.
The initial Script Section display for the Optimization algorithm shows the following:
% invoke optimization
[x,fval,exitflag,output] = fmincon(wrapperfunc, startingpoint, [], [], [], [], $ANS_MINVAL, $ANS_MAXVAL, nlcon, options)
The initial Script Section Options display shows the following:
% customers can add their own options below
options = optimset(options, 'display', 'iter')
options = optimset(options, 'Algorithm', 'interior-point')
% options = optimset(options, 'PlotFcns', @optimplotfval)
You can modify the script to extend and customize the optimization to your needs. You must ensure that the script follows MATLAB syntax. For instance, by modifying the optimization script you can:
- Change the optimization algorithm (for example, call fminsearch instead of fmincon).
- Change the parameters/options of the optimization algorithm (see the MATLAB documentation for details).
- Specify a plot function to provide graphical output during optimization.
- Specify a user-defined output function to be called at completion or per iteration.
Symbols
When modifying the MATLAB code, you can use symbols to represent values from the optimization setup. The symbols and their definitions are listed below.
|
$ANS_VARIABLE_LIST: |
List of variables we are optimizing. |
|
$ANS_STARTING_POINT: |
Vector of starting values of variables used in the optimization. |
|
$ANS_MAXITERATIONS: |
Maximum number of iterations specified in optimization setup. |
|
$ANS_MINVAL: |
Vector of minimum values from optimization setup. |
|
$ANS_MAXVAL: |
Vector of maximum values from optimization setup. |
|
$ANS_MINSTEP: |
Vector of minimum step sizes from optimization setup. |
|
$ANS_MAXSTEP: |
Vector of maximum step sizes from optimization setup. |
|
$ANS_A_MATRIX |
Matrix of linear constraint coefficients (left-hand side) generated from optimization setup. |
|
$ANS_B_MATRIX |
Matrix of linear constraint bounds (right-hand side) generated from optimization setup. |
The linear constraints as generated for MATLAB have the form [A][x] <= [B], where [A] is the coefficient matrix, [x] is the variable list matrix (column vector), and [B] is the bounds matrix (column vector).
While modifying the script, make sure that the script follows MATLAB syntax.
MATLAB Optimization Script Template
The script template shown in the Script Section is as follows:
% make sure platform matches
if strcmp(computer, '$ANS_EXPECTED_PLATFORM') ~= 1
h = msgbox('32/64 platform does not match calling application, exiting')
uiwait(h)
exit
end
% add installation dir to search path so .mex file can be found
originalpath = addpath('$ANS_EXEDIR')
% connect back to opticomengine
callbackinterface = optimex('connect', '$ANS_CONNECTIONSTRING')
% set up optimization
% variables are: $ANS_VARIABLELIST
startingpoint = $ANS_STARTINGPOINT
options = optimset('MaxIter', $ANS_MAXITERATIONS)
iterationCallbackWrapper = @(x, optimValues, state) optimex('notifyiterationcomplete', callbackinterface, x, optimValues.fval, state)
options = optimset(options, 'OutputFcn', iterationCallbackWrapper)
% halt execution so debugger can be attached
% h = msgbox('attach debugger if desired')
% uiwait(h)
% attributes that user can pass to optimization algorithm
% variables are: $ANS_VARIABLELIST
% this is the objective function which returns cost
wrapperfunc = @(x)optimex('eval', callbackinterface, x)
% this is our non linear constraint function, returns no constraints
returnempty = @(x)[];
nlcon = @(x) deal(returnempty(x), returnempty(x));
% DO NOT EDIT THIS LINE - START OPTIONS SECTION
% customers can add their own options below
options = optimset(options, 'display', 'iter')
options = optimset(options, 'Algorithm', 'interior-point')
% options = optimset(options, 'PlotFcns', @optimplotfval)
% DO NOT EDIT THIS LINE - END OPTIONS SECTION
% DO NOT EDIT THIS LINE - START OPTIMIZATION ALGO SECTION
% invoke optimization
[x,fval,exitflag,output] = fmincon(wrapperfunc, startingpoint, $ANS_A_MATRIX, $ANS_B_MATRIX, [], [], $ANS_MINVAL, $ANS_MAXVAL, nlcon, options)
% DO NOT EDIT THIS LINE - END OPTIMIZATION ALGO SECTION
% write exit message to Ansoft message window (warning=0,error=1,info=2)
optimex('postansoftmessage', callbackinterface, 2, output.message)
% notify opticomengine that optimization is finished
optimex('optimizationfinished', callbackinterface, exitflag)
% restore original path
path = originalpath
% note: comment below line if you want MATLAB to remain
% running after optimization
exit