State-Space Method: State Equations and Output Equations
The vector of state equations:
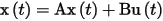
Where:
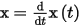
This gives the rate of change of the state variables (responses), computed as a weighted sum of the current state vector and the input vector. Matrix A, the state matrix, contains the frequency-dependent poles of the system. Matrix A has dimension N by N. Matrix B, the input matrix, contains the weights applied to the input vector. Matrix B has dimension P by N.
From the time derivatives of the state variables x(t) one may calculate the values of x(t + Dt) using the vector of output equations:
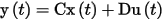
The output vector is a weighted sum of the current state vector and the input vector. Matrix C, the output matrix, contains the weights applied to the state vector. Matrix C has dimension Q by N. Matrix D, the feedforward matrix, contains weights applied to the input vector. Matrix D has dimensions Q by P.
