Inductance
Inductance is the property of a circuit element to oppose a change in current. The time-varying magnetic field produced by a change in current causes an induced voltage to oppose the original change in the magnetic field. Self-inductance is the property of a circuit whereby a change in current causes a change in voltage. It is represented by L and is calculated as:
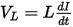
where:
VL = the induced voltage, in volts
L = the value of self-inductance, in henries
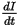 = the rate of change in current, in
amperes per second
= the rate of change in current, in
amperes per second
The unit of inductance is henries (H). One henry is the amount of inductance that is required for generating one volt of induced voltage when the current is changing at the rate of one ampere per second. One henry is equal to one volt-sec per ampere.
