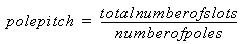Windings Basic Terminology
Conductor
A conductor refers to a half turn of a coil. A conductor may be formed with one insulated wire, or with several strands of insulated wires.
Strands
A conductor may consist of several wires of same or different sizes stranded together. The number of strands is also called number of wires per conductor. The conductor current may not uniformly distribute among all wires, but the current density is uniformly distributed.
Coil
A coil is wound with several turns, each turn consisting of two conductors. Coils are generally wound with insulation-wrapped electromagnetic wire continuously on a winding mold. However, coils with single-turn for heavy current are often formed with two separate thick conductors. A thick conductor is hammered onto the winding mold to form a half-coil. The linear part of a conductor imbedded into a slot of iron core is termed effective side.
Coil Pitch
The number of slots of the armature iron core spanned by the two effective sides of a coil is termed coil pitch, denoted by y. For instance, if the side of a coil in the 1-st slot spans 8 slots and is connected to the side of the coil in the 9-th slot, the coil pitch of the coil is y = 8.
|
Full coil pitch: |
coil pitch = pole pitch |
|
Short coil pitch: |
coil pitch < pole pitch |
|
Long coil pitch: |
coil pitch > pole pitch, usually used in variable-pole multiple-speed machines |
|
Pole pitch: |
distance between two contiguous poles measured in number of slots.
|
Coil Set
The coils belonging to the same phase under one pole are connected in series as a coil set.
Winding
The coils or coil sets of a phase are connected according to certain rules to form a phase winding. A phase may consist of several branches connected in parallel. Every branch must produce exactly the same back emf and must have the same resistance. As a result, the phase winding current is uniformly distributed among all branches.
In summary, a winding may be connected with several branches in parallel; each branch consists of one or more coil sets connected in series; a coil set may have several series coils; a coil is wound with a number of turns; a turn is formed by two conductors; a conductor may be stranded by one or more same- or different-size wires.