Virtual Forces (Electrostatic)
To compute the virtual force on an object, the electrostatic field simulator uses the principle of virtual work. In the structure shown below, the force on the bottom plate (plate B) in the direction of the displacement, x, is given by the following relationship:

where W is the stored energy of the system,
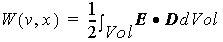
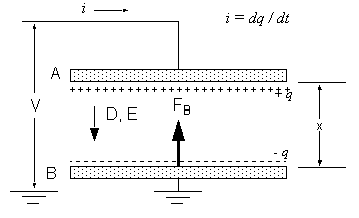
Unlike the classical virtual work method, the plate is not actually moved during the numerical process of the force computation. Instead, only the triangles that lie along the outside surface of the object are virtually distorted. W and its derivative, dW/dx, are calculated from a single field solution using finite element interpolation functions.
The virtual work method is only valid for objects surrounded by the materials air or vacuum. In the electrostatic solver, a threshold of tolerance = 1.e-7 (compared to the permittivity of vacuum/air) is used to determine if the material is vacuum/air. When an object is surrounded by materials other than air or vacuum the Maxwell stress tensor method is applied to calculate the force acting on the object.
