Simplify Command
Use the Modeler > Model Preparation > Simplify command to converts a complex MCAD object into simpler primitives which are easy to mesh and solve. The operation can be applied on any selected object and not just imported objects. You can specify the type of simplification as Bounding Box, Primitive Fit, or Polygon Fit.
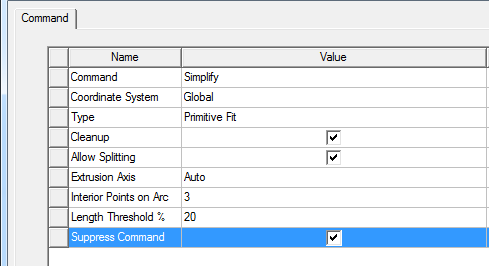
The History tree shows the Simplify command as being applied to the object.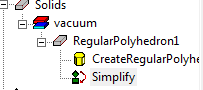
Any parameters you specify in the dialog you can also edit in the Properties dialog for the History tree Simplify command to get a different simplification. The properties display in the docked properties includes only the parameters that are used by your currently selected Simplify command type. None of the parameters of simplify operation accept variables. If you right-click on Simplify for a project that was created for an earlier version, the menu displays and option to Upgrade version. After an upgrade, the option not longer appears. The Properties dialog for the Simplify command allows you to suppress the command.
- Select an object.
- Click Modeler > Model Preparation > Simplify.
This opens the Simplify Bodies dialog box. A drop-down menu lets you select the degree of simplification, from Bounding Box, Primitive Fit, or Polygon Fit. These options are explained below.
This enables the Simplify command on the Modeler > Model Preparation submenu.
Simplify Types
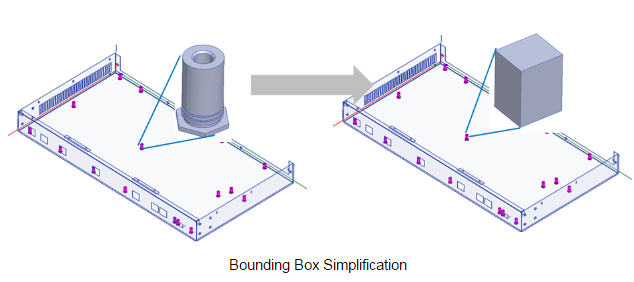
Bounding Box
If you select Bounding Box as the Simplify Type, there are no additional parameters. The object is replaced by its exact bounding box as computed in operation’s coordinate system. You can change the operation CS to get a bounding box in an appropriate orientation. For the Non History Operation options, see below.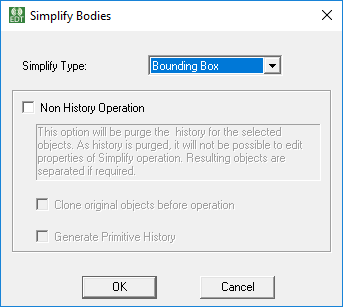
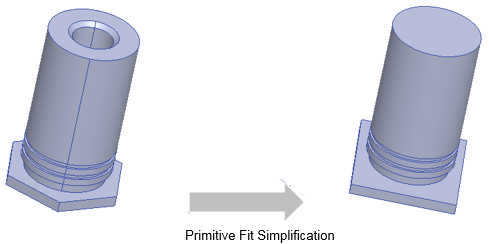
Primitive Fit Simplification
For Primitive Fit simplification the object is replaced by a set of primitives shapes like Prism, Cylinder, Cone and so forth. This simplification type typically produces the simplest geometry with highest number of primitives. Primitive Fit has the following options: Cleanup and Allow Splitting. For the Non History Operation options, see below.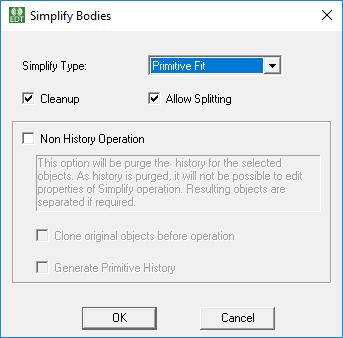
For Primitive Fit, the parameters are:
- Cleanup - This option allows you to clean the model before performing simplification. Cleanup include removing small features like rounds, fillets, and chamfers in a solid body. It is recommended to set this option to get a more simplified result.
- Allow Splitting - This option controls if object should be split during simplification. If this option is selected, complex object will first split into multiple pieces and each piece will be further simplified. Setting this option will result in an object which will match more closely with original object. It is recommended to set this option.
- For the Non History Operation options, see below.
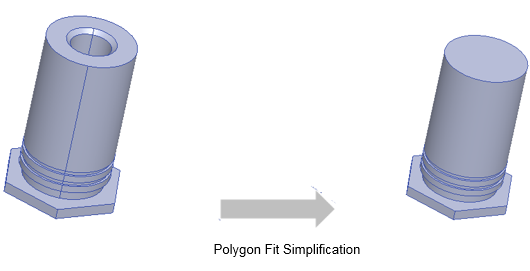
Polygon Fit Simplification
For Polygon Fit simplification, the object is replaced by set of polygon swept along normal and other primitives like box and cylinder. This simplification type typically produces geometry closest to original object with highest number of primitives. If you select Polygon Fit as the Simplify Type, the parameters are Cleanup, Allow Splitting, Extrusion Axis, Interior Points on Arc, and Length Threshold. For the Non History Operation options, see below.
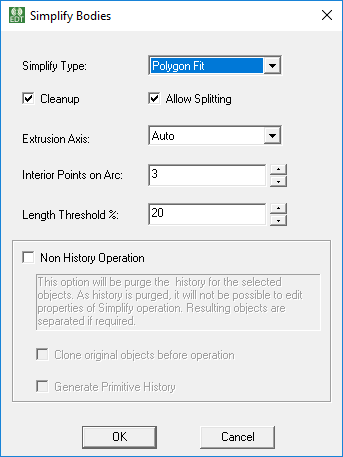
For Polygon Fit, you specify the following parameters:
- Cleanup - This option allows you to clean the model before performing simplification. Cleanup includes removing small features like rounds, fillets, and chamfers in a solid body. It is recommended to set this option to get a more simplified result.
- Allow Splitting - This option controls if object should be split during simplification. If this option is selected, complex object will first split into multiple pieces and each piece will be further simplified. Setting this option will result in an object which will match more closely with original object. It is recommended to set this option.
- Extrusion Axis - This option specified a normal plane in which polygon profile is looked for. The default is Auto which allows an algorithm to determine best possible plane for polygon profile. You can specify a axis to help the algorithm, particularly when there is a draft or chamfer in the extrusion direction. The polygon profile is then swept in the extrusion direction.
- Interior Points on Arc - This specifies number of interior points created when a curve on the polygon profile is represented by line segments. The range is 1 to 100 with default being 3. Total number of points used to represent a curve is 5 when number of interior points is 3. This number specifies the maximum number of interior points to add. The number of points added could be less if the Length Threshold is already met.
- Length Threshold % - This specifies the length of edge as percentage of maximum length of an edge in the profile. It is specified as percentage of maximum edge length. If length of edge is more than the specified threshold, more interior points are added until the number of “Interior Points on Arc” is met.
- For the Non History Operation options, see below.
Non History Operation Options
The Non History Operation options are available for all Simplify Types. 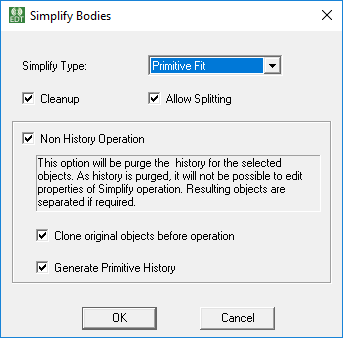
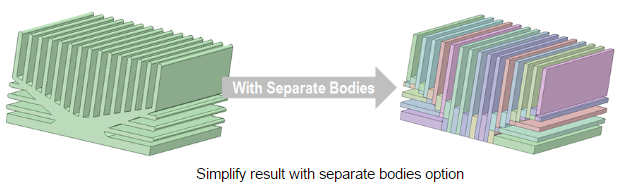
With this option selected, the input body is simplified into multiple primitives (or polygon shapes) and a new part is created for each simplified shape. This option also purges the history of original part and it is not possible Edit Properties of the Simplify operation. You can choose to clone original object before simplification to retain history of original part. You can also choose to generate a primitive history.
Use of Coordinate System
By default, the current working coordinate system is used as the Simplify operation coordinate system, but you can also change active coordinate system through the Simplify command property window or the Property dialog.
