Magnetic Saturation
A material with a non-zero magnetic saturation is considered to be a ferrite. When a ferrite is placed in a uniform magnetic field, the magnetic dipole moments of the material begin to align with the field. As the strength of the applied bias field increases, more of the dipole moments align. The magnetic saturation, Ms, is a property that describes the point at which all of the magnetic dipole moments of the material become aligned. At this point, further increases in the applied bias field strength do not result in further saturation. The relationship between the magnetic moment, M and the applied bias field, H, is shown below.
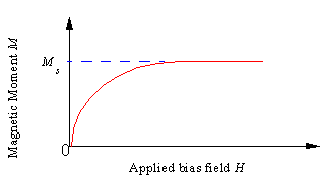
The magnetic saturation, 4pM, is entered in gauss.
