Analysis Approach for Claw-Pole Alternators
Claw-pole alternators (or claw-pole synchronous generators) are widely used in auto industry. They receive mechanical energy at the shaft and transform it into electrical energy.
The stator of a claw-pole alternator is equipped with a polyphase winding. The rotor is comprised of claw poles with the same pole number as the stator winding. The claw poles of the rotor are magnetized by a cylinder winding and/or a cylinder permanent magnet. The spinning rotor creates a rotating magnetic field in the air gap, which produces induced voltage in the stator winding.
The performance of a claw-pole alternator is analyzed based on the frequency-domain phasor diagram, as shown in the figure below.
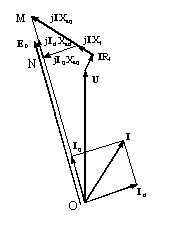
If a claw-pole alternator is equipped with a permanent magnet, the d-axis armature reactance Xad and q-axis armature reactance Xaq are about constant. Otherwise, Xad is a linearized nonlinear parameter, and Xaq is a linear parameter. The d-axis synchronous reactance Xd and q-axis synchronous reactance Xq are calculated directly from the following:
Xd = X1 + Xad
Xq = X1 + Xaq
