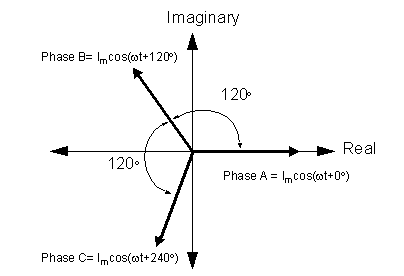AC Current Source
Remember, all AC currents are time-varying quantities in the form I = Im cos(wt + q), where Im is the magnitude of the current and q is its phase angle — the offset of the current from a pure cosine wave. Therefore, when specifying a current or current density, you must enter both its magnitude and phase.
- In a single-phase system, time t = 0 is usually chosen so that the phase angle, q, is zero — that is, the current peaks at t = 0.
- In multi-phase systems involving currents that
are out of phase with each other, time t = 0 is usually chosen so that
one current has a phase angle equal to zero. For example, phase angles
in a three-phase system could be assigned as shown here: