Icepak Post Processing Quantities
The following sections are categories of post processing quantities available to display Icepak results.
Pressure
- Pressure is the relative static pressure of the fluid and is available when flow is computed.
- SurfPressure is the relative static surface pressure of the fluid and is available when flow is computed.
Temperature
- Temperature is available when temperature is computed.
- RadTemperature is the radiation temperature and is available when temperature is computed and you are solving your problem with radiation effects.
- SurfTemperature is the surface temperature and is available when temperature is computed. The surface temperature can be computed only on the surface of model objects; it cannot be computed for plane cuts. Surface temperature results are direct solver values and are usually more accurate compared to temperature results which are interpolated nodal values.
Velocity
- Speed is the magnitude of the velocity vector and is available when flow is computed.
- Velocity Vectors are node-based velocity vectors.
- Ux, Uy, or Uz is the x, y, or z component of the velocity vector and is available when flow is computed.
- SurfVelocity is the magnitude of the surface velocity vector and is available when flow is computed.
- SurfVelocity Vectors are face center-based velocity vectors.
- SurfUx, SurfUy, SurfUz is the x, y, or z component of the surface velocity vector and is available when flow is computed.
Turbulence
- ViscosityRatio is the ratio of the turbulent viscosity to the laminar viscosity. It can be reported if any of the available turbulence models are used.
- WallYPlusis a nondimensional parameter defined by the equation:
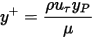
where
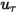 =
= 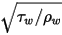 is the friction velocity,
is the friction velocity, 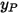 is the distance from point
is the distance from point 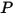 to the wall,
to the wall, 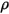 is the fluid density, and
is the fluid density, and 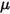 is the fluid viscosity at point
is the fluid viscosity at point 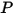 .
. - TKE is the turbulent kinetic energy. It can be reported if the two-equation (standard
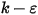 ) turbulence model, the enhanced two-equation model, or the RNG
) turbulence model, the enhanced two-equation model, or the RNG 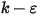 turbulence model is used.
turbulence model is used. - Epsilon is the turbulent dissipation rate. It can be reported if the two-equation (standard
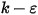 ) turbulence model, the enhanced two-equation model, or the RNG
) turbulence model, the enhanced two-equation model, or the RNG 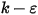 turbulence model is used.
turbulence model is used.
Thermal Conductivity
- Kx, Ky, or Kz is the x, y, or z component of the orthotropic thermal conductivity vector and is available when traces are imported.
- Kx_Centroid, Ky_Centroid, or Kz_Centroid is the x, y, or z component of the orthotropic thermal conductivity at the centroid of a cell and is available when traces are imported.
Joule Heating
- ElectricPotential is available when joule heating is applied to a block boundary condition's bulk conductivity property using a thermal modifier.
- CurrentDensity is current density per unit area.
- CurrentDensityX, Y, and Z are the vector components of the current density per unit area.
- JouleHeatingDensity is the joule heating power per unit volume.
- SurfCurrentDensity is the surface current density per unit area.
- SurfCurrentDensityX, Y, and Z are the vector components of the surface current density per unit area.
- SurfJouleHeatingDensity is the surface joule heating power per unit volume.
EM Mapping
Volume Heat Loss and Surface Heat Loss are imported scalar quantities that are available when EM Loss thermal boundary conditions are defined in the Icepak design.
- VolumeHeatLoss is the imported volumetric EM power per unit volume. It is a nodal quantity.
- SurfaceHeatLoss is the imported surface EM power per unit area. It is a nodal quantity.
Others
- HeatFlowRate is a derived scalar quantity computed from the temperature field. The heat flow can be computed only on the surface of model objects; it cannot be computed for plane cuts or isosurfaces. Two types of heat flow can be computed on an object face:
The heat flux,
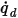 , at a point on a surface is computed from
, at a point on a surface is computed from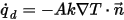
where
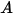 is the surface area of the face,
is the surface area of the face, 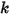 is the conductivity of the material,
is the conductivity of the material, 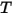 is the temperature, and
is the temperature, and 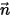 is the normal to the surface.
is the normal to the surface.The heat flow,
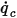 , at flow boundaries is computed from
, at flow boundaries is computed from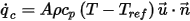
where
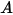 is the surface area of the face,
is the surface area of the face, 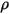 is the density of the fluid,
is the density of the fluid, 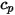 is the specific heat,
is the specific heat, 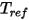 is the default ambient temperature, and
is the default ambient temperature, and 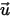 is the velocity.
is the velocity.The Heat flow (into Solid) for a solid surface denotes the total heat flowing into the solid object through the surface. It usually represents the conductive component of the heat transfer at the surface. The Heat flow (into Fluid) for a solid surface denotes the total heat flowing into the fluid domain through the surface.When there is no radiative heat transfer in the domain this value represents the convective component of the heat transfer at the surface.When radiation is included the value represents both the convective and radiative components of heat transfer. In such cases the convective component can be determined by subtracting the radiative heat flow value for the surface from the Heat flow (into Fluid) value.
-
ConductionHeatFlow for a solid surface denotes the total heat flowing into the solid object through the surface. It usually represents the conductive component of the heat transfer at the surface.
-
ConvectiveHeatFlow for a solid surface denotes the convective heat flowing into the fluid domain through the surface.
- HeatTransferCoeff is a derived scalar quantity computed from the temperature field.
The heat transfer coefficient is computed as
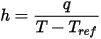
where
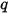 is the heat flux for the surface and
is the heat flux for the surface and 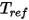 is a reference temperature.
is a reference temperature. - HeatFlux is a derived scalar quantity computed from the temperature field. The heat flux can be computed only on the surface of model objects; it cannot be computed for plane cuts. Two types of heat flux can be computed on an object face:
The heat flux,
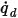 , at a point on a surface is computed from
, at a point on a surface is computed from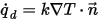
where
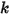 is the conductivity of the material,
is the conductivity of the material, 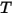 is the temperature, and
is the temperature, and 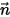 is the normal to the surface.
is the normal to the surface.The heat flux,
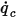 , at flow boundaries is computed from
, at flow boundaries is computed from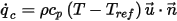
where
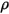 is the density of the fluid,
is the density of the fluid, 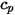 is the specific heat,
is the specific heat, 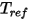 is the default ambient temperature, and
is the default ambient temperature, and 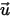 is the velocity.
is the velocity. - MassFlowRate is a derived scalar quantity computed from the velocity field. The flow rate can be computed only on the surface of model objects; it cannot be computed for plane cuts. The sign convention for mass flow values at all flow boundaries (internal and external) is shown such that flow going in the direction of the coordinate axes is positive.
- MassFlux is the mass flow rate per unit area and can only be computed on the surface of model objects.
- RadiationFlow is a derived scalar quantity. It is available if you are solving your problem with radiation effects. It can be computed only on surfaces of objects.
- RadiationFlux is the radiation heat flow per unit area and can only be computed on surfaces of objects. It is available if you are solving your problem with radiation effects.
- VolumeFlowRate is a derived scalar quantity computed from the velocity field. The flow rate can be computed only on the surface of model objects (typically, a fan, vent, or opening); it cannot be computed for plane cuts or isosurfaces. The sign convention for volume flow values at all flow boundaries (internal and external) is shown such that flow going in the direction of the coordinate axes is positive.
- FluidDensity is the density of fluid per unit volume and can only be computed in fluid regions. Fluid density is only available when the density is varying (i.e., when ideal gas model is used or thermal modifier is specified for the density).
