Optimization Variables and the Design Space
Once the optimization variables are specified, the optimizer
handles each of them as an n-dimensional
vector x. Any point in the design space
corresponds to a particular x-vector
and to a design instance. Each design instance may be evaluated via FEA
and assigned a cost value; therefore, the cost function is defined over
the design space (cost(x): 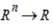 , where n is the number of optimization variables.
, where n is the number of optimization variables.
In practice, a solution of the minimization problem is sought only on a bounded subset of the Rn space. This subset is called the feasible domain and is defined via linear constraints.
