Mesh Generation
Mesh generation is the process by which space-discretization is implemented. During mesh generation, a geometric domain is divided into a number of elements.
The type of the mesh is defined by the shape of the element, which can be tetrahedral, hexahedral, polyhedral, pyramidal, prismatic etc.
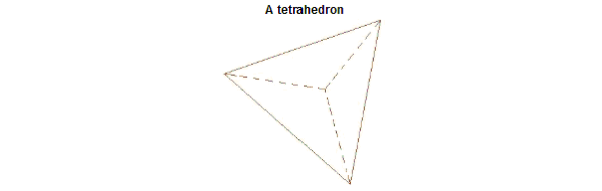
In HFSS, a mesh is a discretization of a continuous domain (geometry) into small three-dimensional tetrahedral and two-dimensional triangular elements. The following figure shows a tetrahedron, which is a solid composed of four triangular faces.
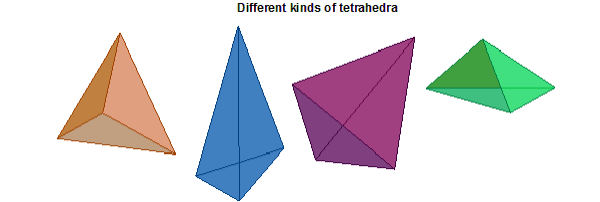
Tetrahedra are the simplex for R3 space, which means that any 3D shape can be decomposed into tetrahedra. Since the process of mesh generation is automatic in HFSS, this mathematical guarantee is necessary for successful mesh generation of arbitrary domains. Therefore tetrahedra (and triangles for two-dimensional surfaces) are used. Tetrahedra can be stretched and pulled (see the figure below), which allows them to fit any arbitrary 3D geometry; so any 3D shape can be decomposed into a number of tetrahedra.
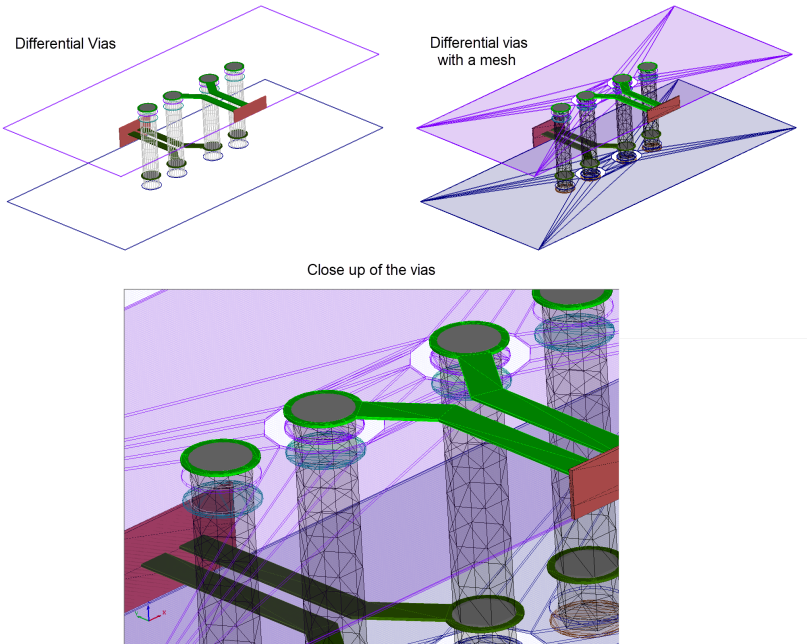
The
following figures illustrate HFSS 3D Layout designs of differential vias before
and after the mesh is created. Notice that the model
is well-represented by the mesh.