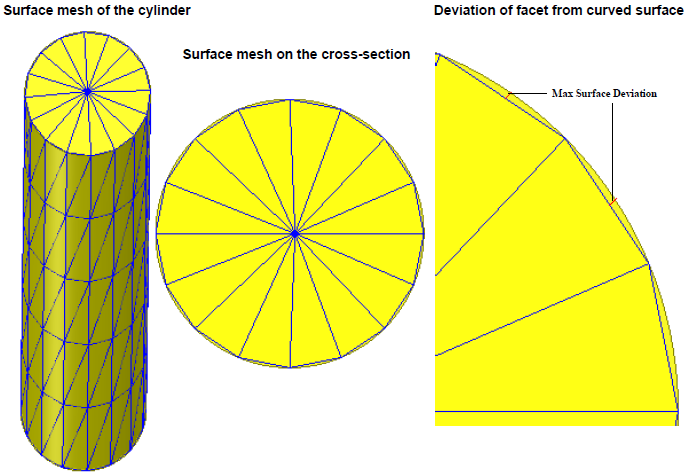
Maximum Surface Deviation (Length)
All curved surfaces are faceted during the meshing process.
A facet is a collection of triangles. There is a small distance between
the faceted surface and the curved surface, which is called surface
deviation. Maximum Surface Deviation is
the maximum value of this distance. The following figures show a meshed
cylinder in HFSS, the cylinder cross-section, and the maximum
surface deviation that occurs near the center of each faceted
triangle. When you use an appropriate value for Maximum
Surface Deviation (length), the curved surfaces are well-represented
to realize the original surface.
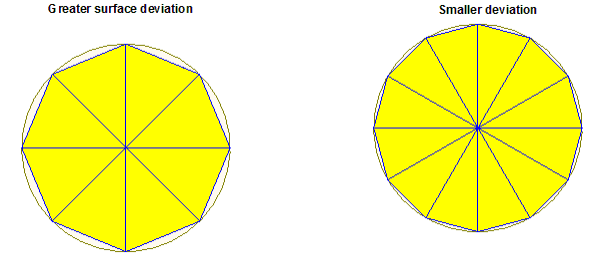
The following figures illustrate how the representation
of a curved surface changes when different values of maximum surface
deviation (length) are used. Smaller values of maximum surface deviation
can result in greater number of faceted triangulations, for more accurate
approximation of the curved surface. However, increasing the number of
triangles causes more CPU time and memory consumption during simulation.
For this reason, use the default settings, since they are adequate for
most circumstances. In the following figure, the cylinder radius is 0.5 mm,
height is 1.5 mm, and the normal deviation angle is kept constant at
45 degrees to illustrate the effects of different maximum surface deviation
lengths.