Axial Ratio
Axial ratio is defined as the ratio of the major to the minor axis of the polarization ellipse.
- Exand Ey are orthogonal complex-valued field components. If either is zero, HFSS treats the field as linearly polarized. However, if neither Exand Ey is zero:
- Compute circular components E- and E+
from:
E- = Ex - jEy
(1)
E+ = Ex + jEy
(2)
- If E+
= 0 or E- =
0 HFSS understands the field as perfectly circular, the axial ratio is
1. Otherwise, for the elliptical polarization case, HFSS determines
the tilt angle t from:
phase(E-/E+) = 2t
(3)
- Rotate the original data to coincide with
the axes of the polarization ellipse.
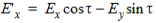
(4)

(5)
- The Axial Ratio AR is given by:
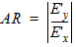
(6)
Because the above definition does not discriminate between major and minor ellipse axes, to enforce the convention that AR< 1, it is necessary to check this condition and if necessary invert the value obtained.
