CTLE Data Parameters
The default, "legacy" implementation uses a first- or second-order filter model, depending on whether one or two poles (respectively) are specified. To enable CTLE, the user gives the linear frequency corresponding to the first pole (f1). Optionally, the user can supply a linear frequency corresponding to the second pole (f2), a zero frequency for the response curve, and a list of allowable DC Gain values. The first pole frequency f1 typically is the lower bound of the high passband. The optional second pole frequency f2 typically is the upper bound. The optional zero frequency fz typically is the beginning of the upslope in the response curve. Here is a simplified diagram:
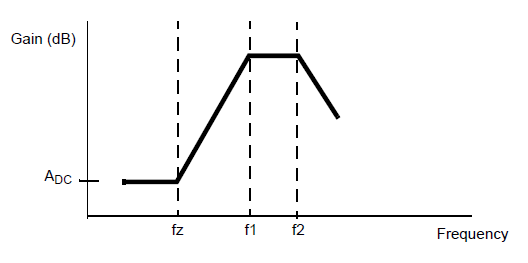
The Circuit solver varies the Gain to find the optimum equalization (maximum eye height) for the channel. The list of gain values can contain one value or several (-infinity dB to 0 dB). If no list of Gain values is supplied, the Circuit solver calculates the optimum CTLE gain between the corresponding linear values, from 0 (equivalent to -infinity dB) to 1 (equivalent to 0 dB). For the legacy transfer function formulas, there are only two poles and one zero. Let:
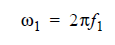
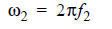
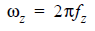
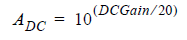
The legacy transfer function with one pole frequency is:
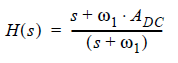
(1)
The legacy transfer function with two poles but no zero is:
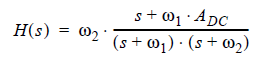
(2)
The legacy transfer function with two poles and a zero is:
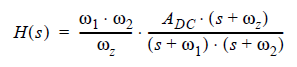
(3)
