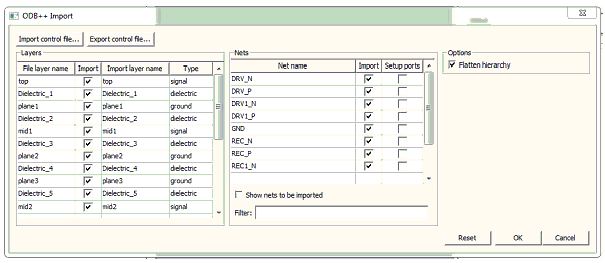
The ODB++ translator is a link to an external DLL that can be accessed by clicking File > Import > ODB++ which opens the import window.
Import and Export Control Buttons
- Import control file opens a window which allows a user to import a chosen control file.
- Export control file writes an xml control file based on the information in the window to the location specified.
Layers Pane
- Import check box specifies which layers to import.
- Import layer name can be edited.
- Type can be changed and identifies the layer type that are used to place each layer in the file (not editable if the layer already exists; for layers that don’t exist, click in the column to see a drop-down menu of choices).
Nets Pane
- Import check box specifies which nets to import.
- The Nets grid control allows users to select the nets to be imported and indicate if pins on that net should be imported as ports.
- Pins that belong to nets with a check in the SetupPorts column become ports when imported.
- Show nets to be imported moves nets to be imported to the top of the grid control.
- Filter involves enhanced wild card filtering is used to select which nets are shown in the window by using wild cards and characters; the two wild cards supported are * and ? (See Regular Expressions for Nets below).
Options Pane
- Flatten hierarchy allows users to select importing the ODB++ with components or flattening the components.
When you have completed selections, click OK and the file is imported into the active Layout window.
Regular Expressions for Nets
You can use regular expressions to search for nets. These match a text pattern and use special constructions to represent strings or single characters.
To use a regular expression, enter the name of the object you want to select in the field, using wild cards when chosen. The following regular expressions are supported:
|
* |
Matches any sequence of characters. For example, net* selects objects net_1a, net_1b, netLength. |
|
? |
Matches any character. For example, net_? selects objects net_1, net_2, net_a, net_b. |
These match a text pattern and use special constructions to represent strings or single characters (e.g., net* selects all pins in nets that start with “net”, net*:1* selects pins with name that start with “1” in the nets that start with name “net”, A*:3? selects pins 31, 32, 33, 34 etc in nets, A1, ACC, AGND, AGND2).
