This topic describes the following OverlapTo commands:
- OverlapToErrors
- OverlapToPolygons
- OverlapToEdges
Input: One or two DV layers (containing polygons)
Constraint (operator and distance)
Measurement region qualifier (optional)
Orientation Qualifiers (optional)
Intersecting Edge qualifier (optional)
Raw/Merged qualifier (optional)
Output: DV layer – Type varies with the command. OverlapToErrors outputs a DV layer containing error clusters. OverlapToPolygons outputs a DV layer containing polygons. OverlapToEdges outputs a DV layer containing edges.
Description: Overlap is the distance between inside edges, of intersecting geometry, that face each other. The single layer version checks the overlap between different geometries on the same layer. The two layer version checks the overlap between geometry on one layer and geometry on the other layer. This is an edge to edge check, not corner to corner, or corner to edge.
This is a symmetric operation. The order of the input layers does not change the results.
Two edges are considered overlapping if the two geometries intersect but neither contains the other and the edges are inside facing. Arrows in the following diagrams indicate edges that are overlapping.
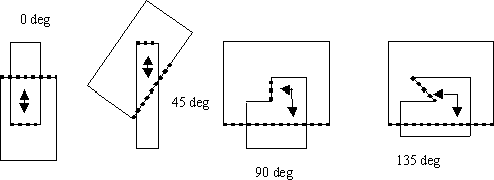
Edges are considered to face each other for overlap checking only if the angle between the inside of one edge and the outside of the other is less than 180 degrees. Collinear edges are not considered facing. The following diagram illustrates angles between inside edges.
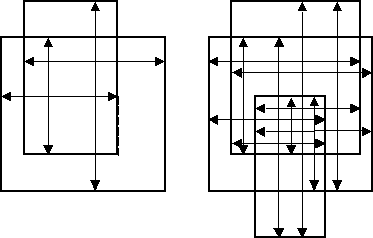
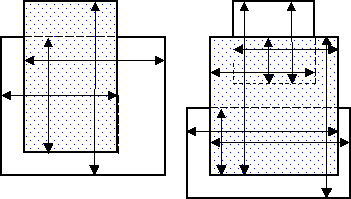
The arrows in the following figures indicate the edge pairs that are checked when considering the facing requirement and using default orientation and intersecting qualifiers: Acute Also, Not Obtuse, Parallel Also, Not Perpendicular, and Not Intersecting.
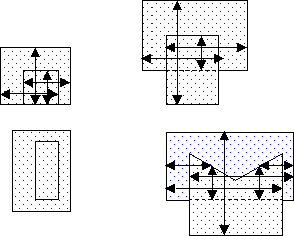
Single Layer Overlap
Two Layer Overlap
The first layer has the dot fill pattern and the second layer is empty. The command looks for the overhang of dot geometry from white geometry.
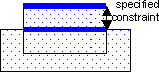
OverlapToError results are clusters of segments that meet the specified constraint. Each error segment indicates the part of the geometry edge that meets the constraint. The error clusters are returned in a DV layer. The heavy lines in the following example show the portions of edges that are returned as one error cluster.
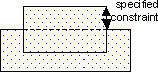
OverlapToPolygons results are any polygons that have at least one edge that meets the specified constraints. The polygons are returned in a DV layer. Both polygons in the following example are returned.
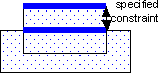
OverlapToEdges results are segments of edges that meet the specified constraints. These segments retain information about the polygon they are created from. This information allows the edges to be used as input to other DV commands. The segments are returned in a DV layer. The heavy lines in the following example show the segments that are returned as edges. They are not clustered, and they retain information about the directions inside and outside of the polygon and sibling relationship.
The constraint amount may be given with or without units. If no units are specified the current default length units are used.
Supported Operators:
Qualifiers may be specified to constrain the edges checked. The defaults, if qualifiers are not specified, are Round (measurement region), Acute Also, Not Obtuse, Parallel Also, Not Perpendicular, Not Adjacent, and Merged (geometry).
Example (JScript):
var layer1 = DVChecker.ImportLayer("trace");
var overhangLayer1 = DVChecker.OverlapToErrors(Array("<", "5mm"), layer1,
Array( "Round", "Acute Also", "Not Obtuse", "Parallel Also",
"Not Perpendicular"));
DVChecker.SaveLayer(overhangLayer1, "overhang errors",
"overhang < 5 on trace layer");
var layer2 = DVChecker.ImportLayer("ground");
var overhangLayer2 = DVChecker.OverlapToErrors(Array("<", 5), layer1,
layer2, Array( "Round", "Acute Also", "Not Obtuse", "Parallel Also"));
DVChecker.SaveLayer(overhangLayer2, "overhang errors",
"trace overhanging ground by < 5");
Measurement Region Qualifier
Measurement region qualifier specifies the construction of the region used to test the constraint. There exist the following choices:
- Round: Forms a region with quarter-circle
boundaries that extend past the corners of the edge by the constraint
distance. Round is the default region, if no region is specified.

- Square: Forms a region with right-angle
boundaries that extend past the corners of the edge by the constraint
distance.

- Opposite: Forms a region with right-angle
boundaries that do not extend past the corners of the edge.

Measurement Region Use To Check Constraint
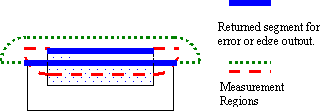
The following figure displays the returned segment for error or edge output, marked in blue, and the measurement regions, marked in red and green, that are used to check the constraint.
Orientation Qualifiers
Orientation qualifiers specify edge or angle orientations that qualify edges to be checked against each other. Up to one choice from each of the following four groups may be used:
- Acute Also
- Obtuse Also
- Not Parallel
- Not Acute
If multiple choices from any of the groups are used, the last choice on the group is used. It replaces any earlier choices of that group in the command.
OverlapToErrors(Array(“<”, 5), layer, Array(“Acute Also, Obtuse Also, Not Parallel, Not Acute));
is interpreted as:
OverlapToErrors(Array(“<”, 5), layer, Array(“Obtuse Also, Not Parallel, Not Acute));
If a choice contains “Only”, that is the only orientation qualifier recognized. Any other orientation qualifiers before or after the first “Only” is ignored.
OverlapToErrors(Array(“<”, “5mm”), layer, Array(“Acute Also, Obtuse Only, Not Parallel, Perpendicular Only));
is interpreted as:
OverlapToErrors(Array(“<”, “5mm”), layer, Array(“Obtuse Only));
Acute filter
- Acute Also – Include the measurement of edges that have an angle between them greater than 0 and less than 90 degrees. Default if none specified.
- Acute Only – Measure only edges that have an angle between them greater than 0 and less than 90 degrees.
- Not Acute – Do not measure edges that have an angle between them of greater than 0 and less than 90 degrees.
Obtuse filter
- Obtuse Also – Include the measurement of edges that have an angle between them of greater than 90 and less than 180 degrees.
- Obtuse Only – Measure only edges that have an angle between them of greater than 90 and less than 180 degrees.
- Not Obtuse – Do not measure edges that have an angle between them of greater than 90 and less than 180 degrees. Default if none specified.
Parallel filter
- Parallel Also – Include the measurement of parallel edges and non-parallel edges. Default if none specified.
- Parallel Only – Measure only parallel edges.
- Not Parallel – Do not measure parallel edges.
Perpendicular filter
- Perpendicular Also – Include the measurement of perpendicular edges and edges of other orientations.
- Perpendicular Only – Measure only perpendicular edges.
- Not Perpendicular – Do not measure perpendicular edges. Default if none specified.
Intersecting Edge Qualifier
Intersecting Edge qualifier determines if two edges that intersect are checked against each other. Intersecting edges are edges that share at least one point. This qualifier is used in conjunction with the orientation qualifiers to determine which edges to check. One of the three choices may be specified.
- Intersecting Also – Check applies to both intersecting and other edges.
- Intersecting Only – Check only applies to intersecting edges.
- Not Intersecting – Check does not apply to intersecting edges. Default if none specified.
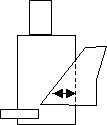
The arrows in the following figure indicate the edge pairs checked using Intersecting Only with the other qualifiers defaulted (Acute Also, Not Obtuse, Parallel Also, Not Perpendicular).
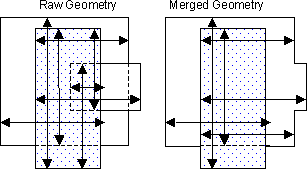
Raw/Merged Qualifier
The Raw/Merged qualifier applies to a DV layer created using the ImportLayer command. Raw specifies the geometry is to be used without first being merged. In contrast, the default setting of Merged specifies the geometry is merged prior to its use.
The arrows in the following figures indicate the edge pairs checked using Raw versus Merged with the other qualifiers defaulted (Acute Also, Not Obtuse, Parallel Also, Not Perpendicular, Not Intersecting).