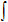Calculating the Average of a Field Quantity on a Surface
Description
This recipe permits you to calculate the average of a field quantity on a Surface geometry, by dividing the Integration of the field value on the surface by the surface area.
Usage Examples
This calculation could be used to determine the average phase of the E-field at a given cutplane through a project, to find the average current on a trace surface, or to calculate the average H-field tangential to a 2D object used as an aperture. The specific example steps below will be for the first usage example mentioned (average phase of an E-field on a surface), but the format for integration on a surface and for finding the area of the surface is identical for the other applications as well.
Prerequisites
The surface on which the integration is to be performed must exist. If the surface is the exterior of a solid object, no customer geometry creation is necessary. If the surface is only a subset of an object’s faces, or a slice through the entire plane of the model not already defined by a separate 2D entity, then you must create a Faces List and/or Cutplane to represent the integration location.
|
Calculator Operation |
Resulting Stack Display |
|
Quantity>{select field quantity} |
CVc : <Ex, Ey, Ez> (E-field used as example) |
|
{Derive desired scalar field data For example: Scal?>ScalarX Complex>CmplxPhase} |
CSc : ScalarX(<Ex, Ey, Ez>) (first operation result) Scl : Phase(ScalarX(<Ex, Ey, Ez>)) (second operation result) |
|
Geometry>Surface...>{select surface} |
Srf: Surface(plane1) (user surface shown may vary) |
|
Value |
SclSrf : SurfaceValue(Surface(plane1), Phase(ScalarX(<Ex, Ey, Ez>))) |
|
|
Scl : Integrate(...) |
|
Geometry>Surface...>{select surface} |
Srf : Surface(plane1) |
|
Unit Vec>Normal |
Vec : SurfaceNormal |
|
Geometry>Surface...>{select surface} |
Srf : Surface(plane1) |
|
Normal |
SclSrf: SurfaceValue(Surface(plane1)... (takes the dot product of the surface with its own normal) |
|
|
Scl : Integrate(Surface(... |
|
/ |
Scl : /(Integrate(SurfaceValue(... |
|
Eval |
Scl : {numerical value} (for this example units are in deg or radians) |