Explanation of L1, L2, and Max norms in Optimization
When you set multiple goals for an optimization, the question arises as to what is actually going to drive the optimizer which is not a multi-objective one. The cost function will have a lot to do with it. The following discussion explains how the cost function is put together when there are multiple goals.
The general goal setting structure in Optimetrics is a logical sentence with the format:
Calculation(i) Condition(i) Goal(i) Weight(i)
The cost function that the optimizer uses is built based on the norm setting as long as there are multiple goals and none of those use the "minimize" or "maximize" conditions. Thus, in this case the error associated with each individual goal (weighted) is combined in a way that is specific for each norm type chosen.
For L1 norm the actual cost function uses the sum of absolute weighted values of the individual goal errors:
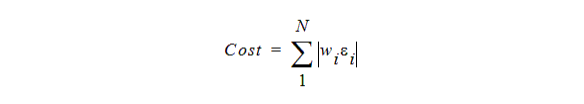
For L2 norm the actual cost function uses the weighted sum of absolute values of the individual goal errors.
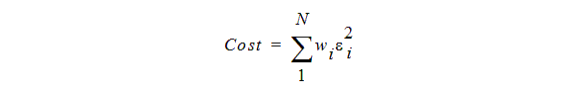
For the Maximum norm the cost function uses the maximum among all the weighted goal errors, which means that cost is always less than zero:
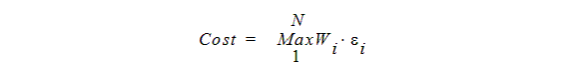
For all the above situations N is the number of individual goals wiei are individual weighting factors and residual error respectively. A minimization of the cost function is performed during optimization since it makes sense to minimize the error in the sense of the chosen norm type.
The graphical representation of the error is possible and depends upon the actual condition being used. If a "<" condition is used, the error can be represented as below:
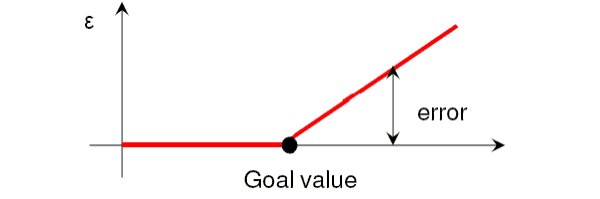
If a ">" condition is used, the error can be represented as below:
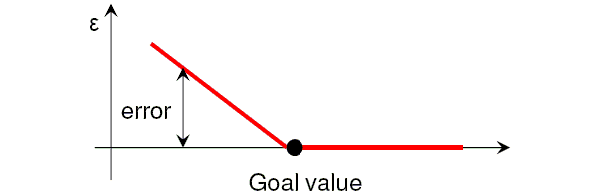
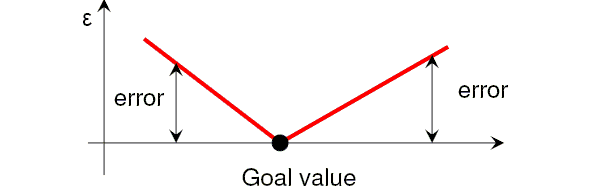
If a "=" condition is used, the error is double-sided and can be represented as below:
The norm type doesn't impact goal setting that use as condition the "minimize" or "maximize" scenarios. Note that when using "minimize" or "maximize" settings for the condition there should be a single goal setting which in this case coincides with the cost function.
