Adding a Cost Function
A cost function can include one or more goals for an optimization analysis. Optimetrics manipulates the model's design variable values to fulfill the cost function. The optimization will stop when the solution quantity meets the acceptable cost criterion.
Following is the general procedure for adding a cost function with a single goal:
- Under the Goals tab of the Setup Optimization or Design of Experiments
dialog box, click Setup Calculations...
The Add/Edit Calculation dialog box is displayed.
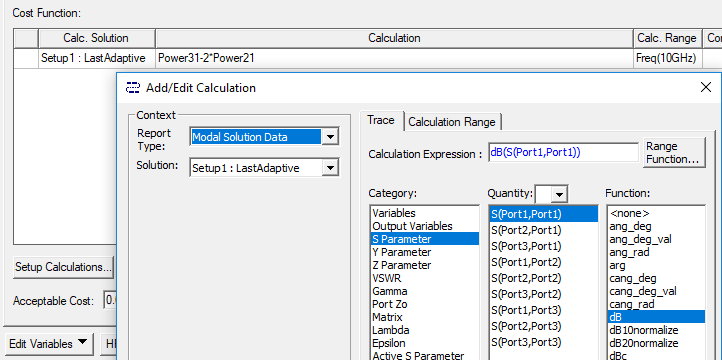
- In the Add/Edit Calculation dialog box, follow these general steps to set up a cost function.
- Set the Context for the calculation.
- Choose the Category of available data type depending upon the Solution type of the design being optimized.
- Select the Quantity to add to the Calculated Expression field. Available quantities depend upon the Category selection.
- You may optionally make a selection from the function list to apply to the calculated expression.
Note:
Because Optimetrics works in SI values, you should use ang_deg_val or cang_deg_val functions which return unitless numbers in degrees rather than ang_deg or cang_deg, which return angular values in degree units but evaluate in radians in Optimetrics expressions. For example, you could Optimize successfully by changing the expression from abs(cang_deg(S(Port2,Port1))) to abs(cang_deg_val(S(Port2,Port1))). See the table of available functions and definitions.
- When the Calculation Expression has the desired equation, click Add Calculation to add the expression to the cost function table.
- Repeat to add additional calculations to the cost function or click Done to exit the Add/Edit Calculation dialog box and return to Setup Optimization.
- To modify the Solution on which the calculation is based, click in the Solution column and select the solution from which the cost function is to be extracted from the drop-down menu.
- To edit the calculation on which to base the cost function goal, select Edit from the drop-down menu.
- In the Condition
text box, click one of the following conditions from the drop-down menu:
<=
Less than or equal to
=
Equal to
>=
Greater than or equal to
Minimize
Reduce the cost function to a minimum value
Maximize
Identify a maximized condition
- In the Goal
text box, type the value of the solution quantity that you want to be
achieved during the optimization analysis. If the solution quantity is
a complex calculation, the goal value must be complex; two goal values
must be specified. The Minimize and Maximize options do
not require you to specify a Goal value.
When Minimize is used as an optimization condition, the value of calculation is used as the cost (there is no target value to compare to). For maximize, the negative of calculation value is used as cost.
- Optionally, if you have multiple goals
and want to assign higher or lower priority to a goal, type a different
value for the goal's weight in the Weight
text box. The goal with the greater weight is given more importance.
If the goal is a complex value, the weight value must be complex; two
weight values must be specified. The weight value cannot be variable
dependent.
Note:
Click the Edit Goal/Weight button to open the Edit Goal Value/Weight dialog box, where you can modify weights for all goals simultaneously and set the Goal Values to expressions.
- Specify other options (such as acceptable cost, noise, and number of passes), and then click OK.
The optimization stops when the solution quantity meets the acceptable cost criterion.
