2D and Circuit Selecting a Far-Field Quantity to Plot
When plotting far-field quantities, the quantity can be a value that was calculated by Electronics Desktop such as antenna gain, a value from a calculated expression, or an intrinsic (inherent) variable value such as frequency or theta.
To select a far-field quantity to plot:
- When you create the report, specify the Report Type as "Far Fields."
- In the Report
window, select one of the following categories for the field setup:
Variables
Intrinsic variables, such as frequency or theta, or user-defined project variables, such as the length of a quarter-wave transformer.
Output Variables
User-defined expressions applied to derive quantities on the original field solution.
Gain
Gain is 4π times the ratio of an antenna’s radiation intensity in a given direction to the total power accepted by the antenna.
Axial Ratio
Axial ratio of the electric field.
Antenna Params
Ansys Electronics Desktop-calculated quantities that include peak directivity, radiated power, accepted power, radiation efficiency, max U, and array factors. For far-field setups, the decay factor for lossy materials is calculated as a constant for all far fields.
Radar Cross-Section (Bistatic RCS)
The radar cross-section (RCS) or echo area (σ) is measured in meters squared and represented for a bistatic arrangement (i.e., when the transmitter and receiver are in different locations). This is represented by:
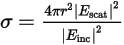
where:
- Escat is the scattered E-field.
- Einc is the incident E-field.
RCS is supported for designs with Plane Incident Waves. RCS is not supported for other types of incident waves.
