Viewing Autoscaling Cluster Details
When you want to view information about an autoscaling cluster or check its status, follow these steps:
Open the project space containing the autoscaling cluster.
In the resource list, click the autoscaling cluster. Its details are displayed.
Cluster State
At the top of the autoscaling cluster view you can see the current state of the cluster. The state is based on processes that may be occurring at this time.

Possible states include:
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| Creating storages | Creating shared storages as defined in the autoscaling cluster wizard. |
| Creating | Virtual machines are being acquired from Azure. |
| Initializing | Virtual machines are being configured. |
| Starting | Virtual machines are powering up. |
| Installing | Applications are being installed and configured. You can view the status of each application installation in the Applications section of the cluster details view. |
| Running |
The head node and static nodes (if any are defined) are running. The cluster can accept submitted jobs. Dynamic nodes are ready to be spun up should a job be submitted. Dynamic nodes may also be running if job execution is in progress. Note: Although dynamic nodes are stopped after
jobs complete, the cluster remains in the Running state, as dynamic
nodes can be started again when more jobs are submitted. The state
of dynamic nodes does not impact the overall state of the
cluster.
|
| Stopping | A user has selected the Stop cluster action and all cluster nodes (head node, static nodes, dynamic nodes) are being stopped. |
| Stopping and updating |
A user has made a change to the cluster which requires the cluster to be stopped temporarily to allow the change to be processed. The head node is still running but all compute nodes are terminated. For example, a user may have chosen to delete a queue from the cluster and the queues are being updated. Once the queue has been successfully deleted, the Queues list will be updated and the cluster will return to the Running state. Note that if any jobs are running when the change is submitted, the job will be allowed to complete before the cluster is stopped and updated. |
| Updating | All cluster nodes are running but a user has made a change to the cluster which is being processed. For example, a queue has been added to the cluster and the cluster's queues are being updated. Once the queue has been successfully created, the Queues list will be updated and the cluster will return to the Running state. |
| Updating storages | A storage is being mounted to or unmounted from the cluster. When the update is complete, the Applications and Mounted storages lists will be updated and the cluster will return to the Running state. |
| Stopped | All cluster nodes including the head node have been stopped. No jobs can be run. |
| Deleting | The cluster is being deleted. Once deleted, it will no longer appear as a resource in the project space. |
Head Node
In the Head node panel you can see the following information about the cluster head node:
- Operating system
- Virtual machine size
- Job scheduler type (for example, Slurm)
- System disk size
- State (Starting, Running, Stopping, Stopped)
- Private IP address
- Custom IT policy extensions applied to the machine (if any), with execution status and logs
- Cost incurred by the head node this month
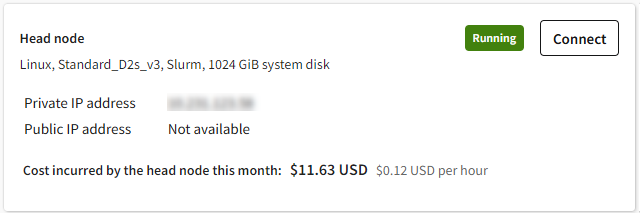
If Ansys HPC Platform Services (HPS) was installed on the head node, HPS is listed as an included service in the head node details along with the storage where cluster applications are installed. You can use the displayed HPS URL to launch the Ansys HPC Manager web app from a web browser.
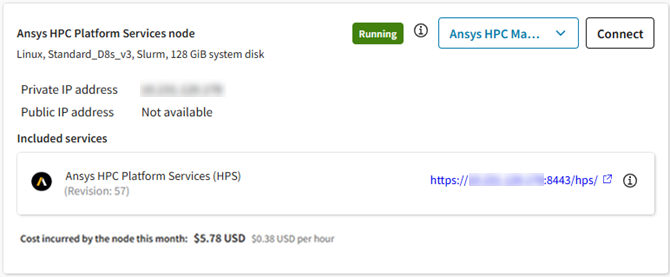
Ansys HPC Platform Services Node
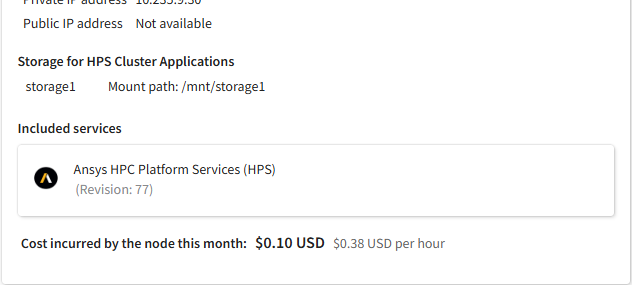
If Ansys HPC Platform Services (HPS) was added to the cluster and installed on a dedicated virtual machine (not the head node), details about that virtual machine are displayed in this panel.
Details about this machine include:
- State (Installing, Starting, Running, Stopping, Stopped)
- Operating system
- Virtual machine size
- Job scheduler type (for example, Slurm)
- System disk size
- Private IP address
- Mounted storage where Ansys cluster applications are installed
- Revision of the installed Ansys HPC Platform Services (HPS) package
- HPS URL (for launching the Ansys HPC Manager web app)
- Cost incurred by the HPS node this month
In this view you can connect to Ansys HPC Manager, Traefik Manager, and Keycloak Identity Management. For more information about these services, refer to the Ansys HPC Platform Services documentation.
If Ansys HPC Platform Services has not been added to the cluster, the panel provides an option to do so if desired. For more information, see Adding Ansys HPC Platform Services to an Autoscaling Cluster in the Administration Guide.
Queues
In the Queues panel you can see the job submission queues that have been defined for the autoscaling cluster. There may be one or more queues defined.
For each queue you can see which application is run when a job is submitted to the queue and how many compute nodes are actively being used for simulation at this moment.
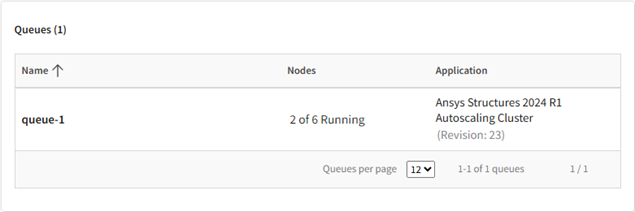
To view information about a queue's configuration, node activity, or costs, click the queue to display additional details. For information on queue details, see Viewing the Details of an Autoscaling Cluster Queue.
Applications
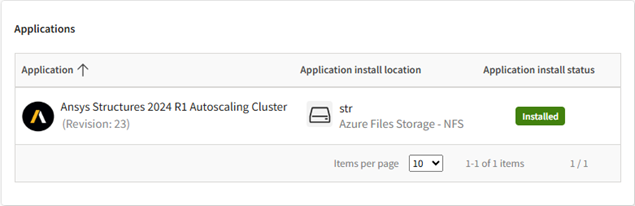
The Applications panel displays a list of applications that have been chosen to be installed on the cluster.
For each application you can see its name and revision number, the storage where the application is installed, and the status of the application installation. For a description of possible statuses, see Checking the Installation Status of Autoscaling Cluster Applications in the Administration Guide.
Mounted Storages
The Mounted storages panel in the autoscaling cluster details displays a list of storages that have been mounted to the cluster.
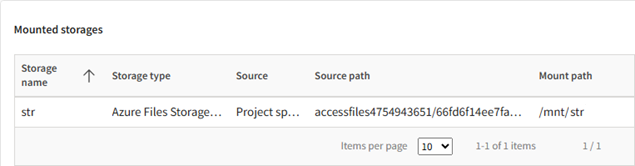
For each storage you can see the following details:
- Storage name. The display name of the storage in Ansys Access on Microsoft Azure.
- Storage type. The type of Azure storage (Azure Files or Azure NetApp Files). For information on the different types of storages that can be mounted to a cluster, see Storage in the Administration Guide.
- Source. Where the storage is located.
- Source path. The path of the storage in Azure.
- Mount path. The path of the mounted storage on the cluster node.
Shutdown Timer for Dynamic Nodes
On the Settings tab of the autoscaling cluster details view you can see the Shutdown timer value that was set for dynamic nodes when the cluster was created.
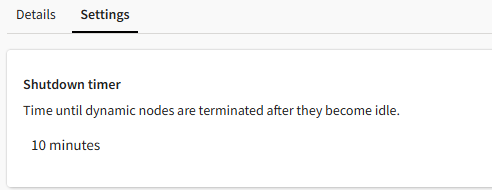
As submitted jobs finish, the nodes that were dynamically provisioned to do the work become idle and remain available for a specified period of time before being shut down. This setting determines how long dynamic nodes can remain available before being shut down.
To see which nodes are currently active and inactive, see Viewing the Details of an Autoscaling Cluster Queue.
Tags
On the Settings tab of the autoscaling cluster details view, the Tags section displays tags that have been applied to the cluster.
Licensing
On the Settings tab of the autoscaling cluster details view, the Licensing section displays the licensing settings being used for provisioning licenses for Ansys applications.
By default, global licensing settings are used unless custom settings were specified when the cluster was created.
The Licensing section is only available if the autoscaling cluster was created on or after November 7, 2025. If the cluster was created before that date, it is using the licensing settings that were specified in the configuration of applications when the applications were selected for installation on the cluster.
You cannot change the license settings. To use different license settings, you must create a new cluster.
If the cluster uses global license settings, and the global license settings are changed, the changes will be applied to the cluster when it is restarted.


